Degree (graph theory)
Degree (even node degree or valence ) is a fundamental concept in graph theory, a branch of mathematics. It describes properties of a node, which can be described by connected edges with him.
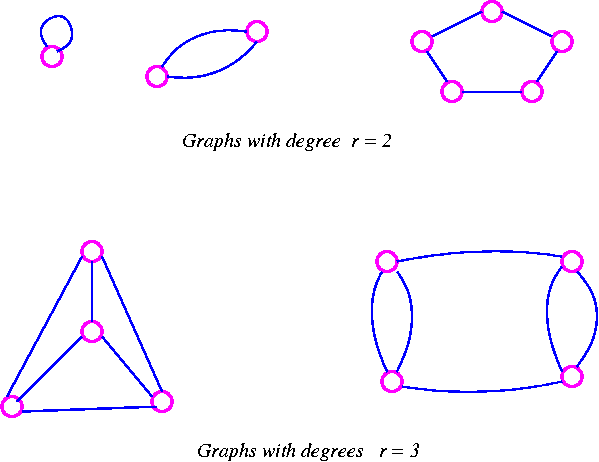
The degree of a graph is the number of edges connecting the nodes to a different node. A sling is thereby counted twice. Often the notation (English degree) is used
If it is clear which graph is, allowed to the index in, and often away.
Definition
Undirected graphs
In an undirected graph in
- Graphs without multiple edges and hypergraphs the number of neighbors of v,
- Graphs with multiple edges, the sum of the multiplicities of all edges incident with v.
The smallest degree of a node in is called the minimum degree of and denote it by, the greatest degree of a node in is called the maximum degree of, this is usually referred to. The average of all node degrees of is called the average degree and denoted by.
Directed graphs
In a directed graph, it is discriminated whether an edge starting at a node or ends. With is called the in-degree of the node v in a directed graph G and its out-degree.
Here, in
- Graphs without multiple edges, the number of predecessors of v,
- Graphs with multiple edges, the sum of the multiplicities of all edges in G of the form ( v, x ).
And in
- Graphs without multiple edges, the number of successors of v,
- Graphs with multiple edges, the sum of the multiplicities of all edges in G of the form (x, v).
A node with no input edges ( ) is called source, a node with no output edges ( ) is called depression.
Related terms
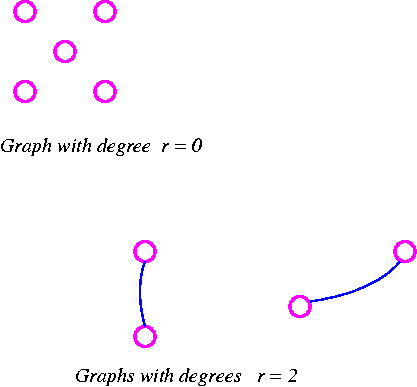
- This is called a knot isolated if it is: in an undirected graph: has no neighbors.
- In a directed graph: no predecessor and no successor has. .
- An undirected graph (or hypergraph ) G is called regular if all of its nodes have the same degree. Possess all of its nodes degree k, this is known as G is k-regular. A 3- regular graph is also called cubic.
- A directed graph G is called regular if all of its nodes have the same input and output degrees. Possess all of its nodes input and output degree k, this is known as G is k-regular.
- A hypergraph G is called uniform if all edges of G have the same number of nodes. Include all edges of G exactly k nodes, it is called G k- uniform.
Properties
- Always apply. Equality holds, for example, in a complete graph.
- The number of vertices with odd degree is stehts straight.
Use
The degree is one of the basic concepts of graph theory and provides many important estimates for graph properties such as the edge coloring number

.svg/2000px-UndirectedDegrees_(Loop).svg.png)