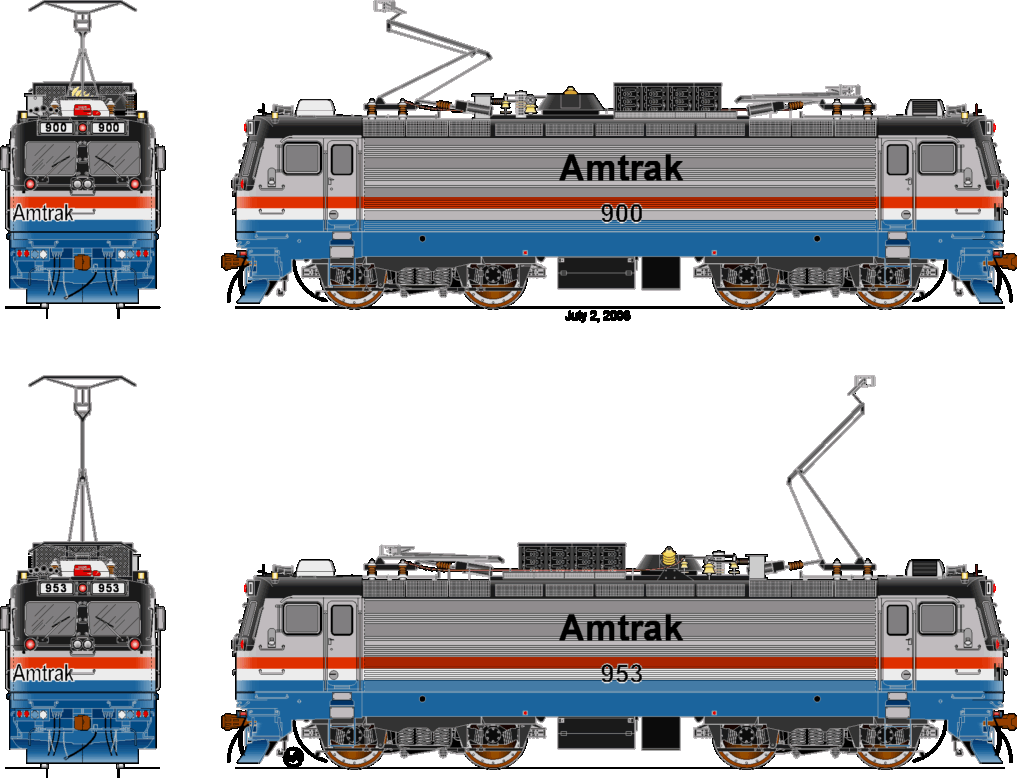
EMD AEM-7
The EMD AEM -7 is a four-axis, electric express locomotive which is in the eastern U.S. for several railway companies, including Amtrak, in use.
History
In the seventies, Amtrak, the U.S. national passenger transport company required for their electrical subnetwork between New York City, Philadelphia / Harrisburg and Washington DC powerful electric locomotives, mainly to replace the aging stock of locomotives of the PRR GG1 class. General Electric responded with heavy six-axle locomotives of the E60. Lack of experience with fast-moving locomotives by the manufacturer led to deficiencies in design and after several serious derailments reduced the regulatory authority, the Federal Railroad Administration, the top speed of the E60 to just 145 km / h (90 mph) as opposed to 193 km / h (120 mph) before. Amtrak was this reduction an eyesore. Since the domestic industry was not in a position to provide suitable locomotives, you looked around in Europe. Both from France ( CC 21000 ) and Sweden ( c4 ) imported to a prototype, both of which have been thoroughly tested after extensive renovations. The French locomotive was renumbered X996, X995 Swedish.
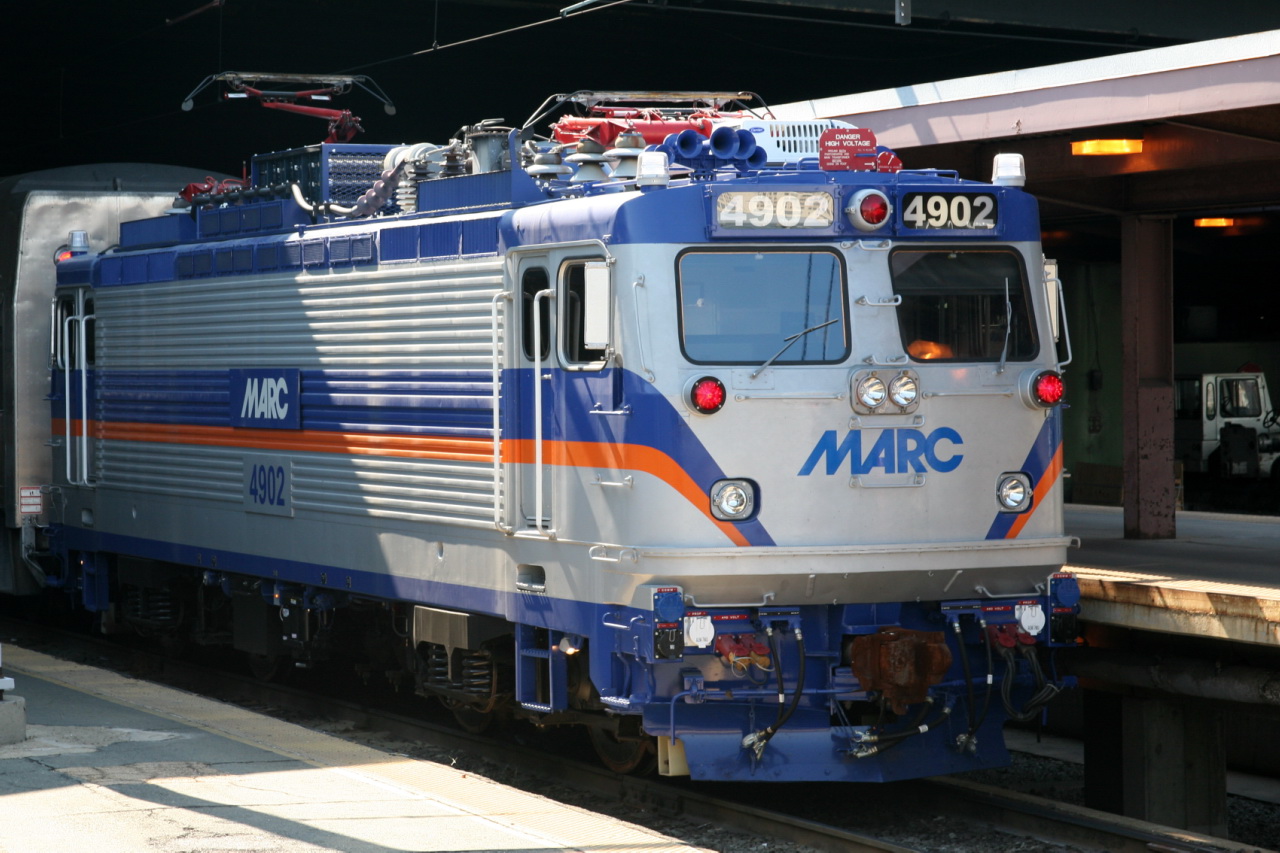
Ultimately, the four-axle c4 proved suitable for the fast passenger, why ASEA was awarded the contract. Amtrak ordered 30 vehicles in 1977, first in 1980 another 17 were commissioned. While the bogies, the electrical equipment and major mechanical components was imported from Sweden, presented the Budd car bodies forth. The final assembly took place at EMD. The first locomotive went into operation in 1979; another 46 were followed until 1982 and helped phase out the aging GG1 quickly. 1987 ordered Amtrak again seven of which were delivered in 1988. MARC, a transport company from Maryland in 1986 ordered four pieces, SEPTA from Pennsylvania a year later seven. Due to the corrugated side walls and the fires in rolling stock failures, the locomotives were quickly given the nickname " toaster ". The AEM - 7 is a multi-system locomotive and can therefore be used in the entire North - East corridor; Today it forms the backbone of passenger transport on electrified routes of Amtrak.
AEM - 7AC
, 1999, Amtrak and Alstom a modernization program. The locomotives now AEM - 7AC mentioned got a new electrical equipment with AC drive and new cabs to name the most important changes. The power increased to 6 MW, which the locomotives now can pull trains with up to 12 cars - this two AEM -7 were previously necessary. 29 locomotives have now been converted.
ALP -44
NJ Transit, one of the largest transport companies in the United States, ordered between 1990 and 1996 a total of 32 locomotives of the ALP -44, SEPTA another. The ALP -44 is basically identical to the AEM -7, but based on the recent Swedish Rc6 and Rc7. The performance data correspond to those of the AEM -7; ALP was controlled by a microprocessor 44 from the beginning. Outwardly, the two types look very similar, the ALP -44 has slightly different roof vent.