Melaleuca alternifolia
Australian tea tree ( Melaleuca alternifolia ).
The Australian tea tree ( Melaleuca alternifolia ) is a plant of the genus Myrtenheiden ( Melaleuca ) in the myrtle family ( Myrtaceae ). Some species of this genus, but also from the genera Baeckea, Kunzea and Leptospermum are called tea tree. From the tea tree species Teebaumöle be recovered by distillation.
Occurrence
This Australian species has its home in New South Wales and Queensland. There, the Australian tea tree grows along rivers and in swamps.
Description
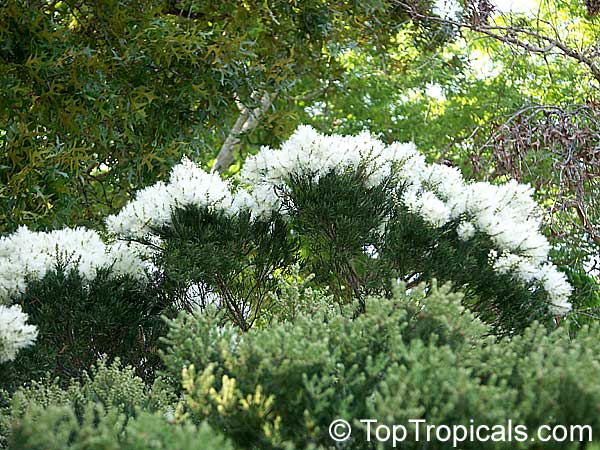
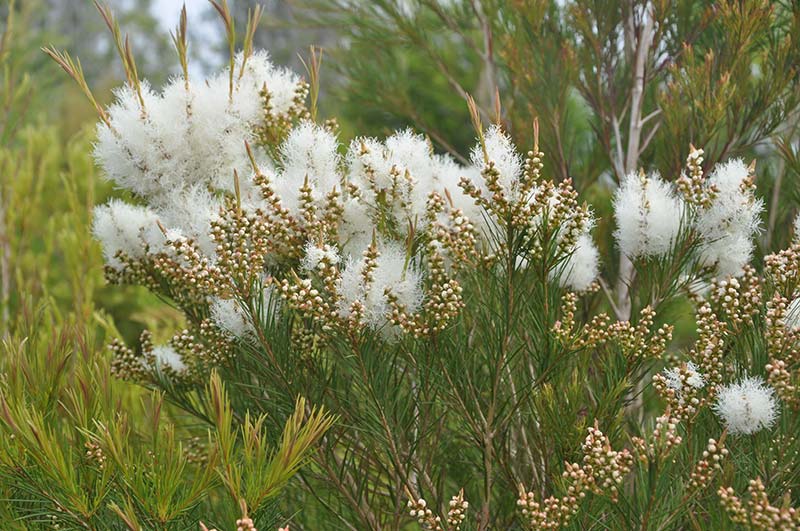
The Australian tea tree ( Melaleuca alternifolia ) is an evergreen shrub or small tree, the growth heights of up to 7 ( to 10) achieved meters. It has a white, papery bark. The bark of young twigs and buds are hairy silky; the bark of older branches is bald. The constantly up against whorls arranged leaves are lanceolate, straight to curved like a sickle, about 1 to 3.5 cm long and 1 mm wide. The petiole is only about 1 mm long.
The many-flowered, aged men, 3 to 5 cm long inflorescences work by many white stamens of flowers like dense whitish fuzz. The radial symmetry, hermaphrodite flowers are fünfzählig. Five small sepals are fused with Roehrig a Chalice tube is 3-4 mm long with broad, short calyx lobes. The free, white petals are 2-3 mm long. The 30 to 60 white stamens are borne in bundles of five; they are about 2 cm long and the short anthers are like claws. The thick pen has a length of about 3 to 4 mm and terminates in a capitate scar. It blooms in the spring.
The cylindrical, hard capsule fruit has a diameter of 2 to 4 mm.
History
The English common name of Melaleuca alternifolia, "Tea Tree", was born 1770. James Cook, at that time Lieutenant of the British Royal Navy, landed with his " HMS Endeavour" in Botany Bay on the east coast of Australia. Cook led his team on an expedition into the dangerous by numerous snakes swamp region. There he found dense groves of trees with aromatic scented leaves. The expedition was also a botanist, Sir Joseph Banks, with it, the leaves of these trees collected and took them to further investigations to England. Lieutenant Cook called tea tree or tea plants because their leaves when they were cooked, a pleasantly spicy and refreshing tea revealed. Cook and his men watched as the local population leaves and bark of the tea plant processed. He then made a decoction of Teebaumblättern produce. This he successfully advocated for the treatment of various skin diseases, as frequently occurring in ship crews as a result of vitamin deficiency.
Between 1920 and 1930, researchers used science deals with the tea tree oil. At that time, researchers were looking for non-toxic products possible at the same time high antiseptic and healing effects. At the beginning of the 1940s, the oil was very popular in Australia as a local antiseptic. Ten years later, but it has been displaced almost completely by penicillin. In the 1970s, the natural substances regained an increasing popularity. And scientific findings contributed to a rapid increase in the production at: 1987 about 80 tons, 750 tons by 1992.
Tea Tree Oil
Is used the essential oil of the leaves and branch tips. It is obtained by steam distillation. Tea tree oil is due to its antiseptic, bactericidal and fungicidal effect use in dermatology (eg in the treatment of acne, dandruff and psoriasis, fungal infections, molluscum contagiosum, muscular pain, open wounds, rheumatism, smoker's cough and varicose veins ), is listed in the European Pharmacopoeia but there is no certain indication due to missing finished medicines.
Subjecting tea tree oil gas chromatographic analysis, we recognize that tea tree oil is a mixture of about 100 substances. These ( )- terpinen-4- ol ( about 40 %), α -terpinene ( 20 %), terpinolene, terpineol ( 3 to 4 %), pinene, myrcene, phellandrene, p- cymene, limonene, 1 ,8- cineole. Tea tree oil has a very strong antimicrobial effect. Compared to the relatively toxic phenol is the tea tree oil 11 to 13 times more effective, and thus, for example, much more bactericidal than eucalyptus oil ( phenol coefficient is about 3.5 ).
The risk of the development of contact allergy is considered critical, triggers are different proportions of oil ( d- limonene and α -terpinene ) and their oxidation products ascaridol and 1,2,4- Trihydroxymenthan. The older the oil, the greater the risk. After four days the oxidation process of the oil begins. The amount of allergen increases and particularly on vorerkrankter skin can cause contact dermatitis .. Up to three percent of those tested were sensitized to tea tree oil in 2003.
Applications
Tea tree oil is used in many dermatological preparations: in shampoos, hand and body creams (especially for blemished skin, acne), in deodorants, bath additives, soaps, toothpaste, mouthwashes. Fungal and bacterial infection of the skin (eg, acne, athlete's foot) mostly preparations containing 5 to 10 % tea tree oil can be used. For applications in the oral cavity tea tree oil must be highly diluted. The preservation of many cosmetic products is possible with tea tree oil.
Also in animal care are external applications of tea tree oil known, overdoses or very frequent treatments should be avoided as in humans. If you want to apply tea tree oil on animals is necessarily the veterinarian should be consulted. Due to the content of terpenes and phenols the tea tree oil as other essential oils is just as toxic to cats. The application does not end rarely fatal for the animal. Typical symptoms of the " tea tree oil poisoning " are trembling, staggering, restlessness and general weakness.
The Australian natives used tea tree oil on open wounds, skin infections, colds, inflammation of the gums and the lice infestation.
Poisoning cases, contraindications by contact allergies
Poisoning cases are also known in tea tree oil. Contact eczema develop very common when tea tree oil undiluted and over a longer period of time ( about 3 years) applied to the skin. The allergenic components are mostly terpinene and aromadendrene, rare terpinen- 4-ol, phellandrene, p- cymene. Caution is also required with persons with a skin hypersensitivity. For boys who have not yet arrived at puberty, the application of tea tree and lavender oil to the growth of the mammary glands can lead (gynecomastia ). This is attributed to an estrogenic and anti- androgenic activity of tea tree oil.
More tea tree species
More tea tree species in the same genus are:
- Kajeputbaum, Cajeputbaum ( Melaleuca cajuputi )
- Silver Tree niaouli, Kajeputbaum, Cajeputbaum ( Melaleuca leucadendra (L.) L.)
- Melaleuca linariifolia
- Niaulibaum ( Melaleuca quinquenervia )
- Melaleuca uncinata
- Niaulibaum Melaleuca viridiflora
Congeners oils
Congeners oils with fungicidal effect of related species, in addition to tea tree oil in descending order of effectiveness:
- Manuka
- Kanukaöl
- Eucalyptus oil
- Cajeput
Also fungicidal effect has propolis, which is produced by bees for germ -free attitude of their hives from tree buds. These substances are available in the pharmacy.
Swell
- New South Wales Flora Online, Melaleuca alternifolia, accessed on 19 October 2010
- Allergy, environment, health, tea tree oil, April 2010, accessed on 19 October 2010


.jpg)





_flowers.jpg)
