Relational frame theory
The reference frame theory (English: Relational frame theory ( RFT) ) is a psychological theory of human language and cognition. It was mainly developed by Steven C. Hayes and Dermot Barnes - Holmes in the early 80s. It is based on the philosophical roots of functional contextualism and deals with cognition and language and their interaction. Another important source is the theory of linguistic behavior by Burrhus Frederic Skinner.
Overview
The reference frame theory has been presented for the first time in 1985 during the conference of the Association for Behavior Analysis (see above, p 98), the first publication in 1989 as a book chapter. 2001 was finally published the first book on the subject. The Association for Contextual Behavioral Science ( ACBS ) was founded in 2005.
The overall goal of behavioral research, which builds on the reference frame theory is to integrate a number of seemingly different psychological phenomena, including stimulus equivalence, naming, comprehension, analogy, metaphor, and usually follow was. The defining core element in all these and many other language activities is the idea that organisms can learn, relationally respond arbitrarily to various stimulus events. In addition, to obey the laws of any learning or amplifier analysis such " answers ".
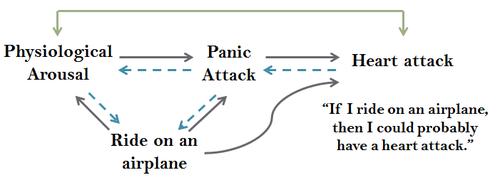
The reference frame theory treats relational responses as generalized amplifier. This points to the formation of multiple copies in the past. The various types of relational responding, called frame of reference that defines three properties: Reciprocal reference ( bi-directionality ), combinatorial reference and transformation of stimulus functions. Reference are arbitrarily applicable, but are typically not necessarily arbitrarily applied in natural language context. In simple terms, the reference frame theory sees socializing relationships as learned behavior. This allows for a response to an event ( a stimulus ) with simultaneous reference to a different event ( stimulus) without both events ( stimuli) were ever brought directly related to each other. Example: I avoid fat sausages, even without eating at or after to have ever experienced a heart attack. This may happen because of a rule in my head like " Beware of unsaturated fatty acids, otherwise you risk a heart attack ".
The most important application of the reference frame theory is the Acceptance and Commitment Therapy.
Support experienced by the reference frame theory currently over 150 scientific studies. Simon Dymond and colleagues searched the literature databases for articles to reference frame theory. They found 174 articles that were published in 1991-2008 in journals with peer review. 112 of these items ( or 64 %) were non- empirical work, at 62 (36%) it was empirical contributions. Since 2001, the number of items increases considerably.
This evidence is weakened by difficulties in its application to relational learning in children.
Within the behavioral analysis, the reference frame theory is controversial. Among other things it is accused of epistemological realism a departure.
An alternative theory, which also deals with derived stimulus relations, the primary process theory of Sidman, makes as opposed to the reference frame theory, no distinction between humans and other animals.
Characteristics of reference
There are three main characteristics of the in-relation - translation as a learned behavior class: