Respiratory therapy
Respiratory therapy can mean two different things: Once the treatment of breathing ( = clinical, medical respiratory therapy ) and on the other hand, treatment with the breath ( = respiratory therapy as a psychotherapeutic or physiotherapeutic procedures).
- 2.1 variants
Respiratory therapy as the treatment of respiratory
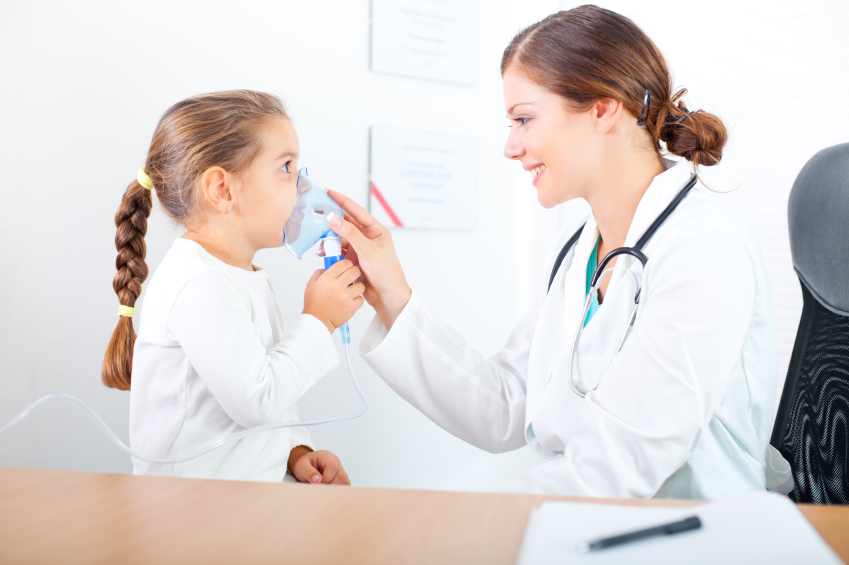
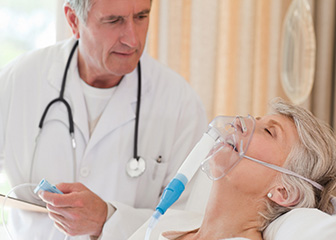
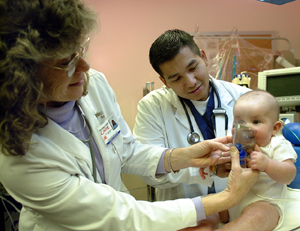
The clinical (medical ) Respiratory therapy deals with the diseases and disorders of the lungs and vocal apparatus. She works both prophylactically and nachbehandelnd. The respiratory therapy has as main objectives the following:
- Pneumonia prophylaxis
- Secretion solution and transport
- Stabilization / construction of a stable bronchial system, especially in obstructive diseases ( chronic bronchitis, asthma, etc.)
Also the breathing training is part of the respiratory therapy. It refers to various exercises to improve lung capacity. This was primarily the chest muscles are strengthened and practiced techniques for increased abdominal breathing.
Effect
An effective respiratory therapy should help to reduce breath -retardant resistors, degradation of incorrect breathing forms of movement, secretion of solution for ventilation increase, to strengthen the respiratory muscles and a general increase in performance.
Variants
- Breath, voice and speech training by the method Schlaffhorst and Andersen: The breath is seen as a link between the autonomic and somatic level of the client. It is intended to improve the breathing of the voice and the movement.
- Buteyko method: a method that guides the patient to less conscious breathing and relieve want as asthma.
- Functional respiratory training after Julius Parow and Margot Scheufele - Osenberg: Based on the circumstances, a logical scientific knowledge about the movements of the diaphragm and the diaphragm supporting muscular processes of the body, it is to restore the natural respiratory function.
Respiratory therapy as self-awareness / self-help
Respiratory therapy is one of the so-called alternative therapies.
Users expect that all of the body functions of a human breath is linked to the most intense of all the other layers of man. In the reticular formation, a complex network center in the depths of the brain stem, all information would flow together, resulting in the body or brain. Every little charm, coming from outside or inside alters to breathe the way. Working through the breath could therefore so is the thesis are achieved and also harmonizes each level of the people.
- Breathing react sensitively and directly on psychological and physical changes. At the same time it is the only body function that can be controlled at will, even though they instinctively runs continuously.
- There would be mechanical and nervous interactions between the respiratory movement and a variety of body organs and their functions;
- The respiratory movement influences the cardiac function and the blood stream; Supply of oxygen, carbon dioxide levels, ion concentration and thus the metabolism
- Breathing influencing on the level of the central nervous system, the conscious processes of the people and thus be sensational and affective life.
There are numerous forms of respiratory therapy, which differ less in their objective, as in their methodology. Thus, some methods work with the so-called " unconscious breathing " of the client, with the other "intentional breath" or " approved breath".
Variants
- Work of breathing by Cornelis Veening: One based on the psychology of Carl Gustav Jung's respiratory therapy that offers a physical and emotional development a way of " inside out " so that " man is the will, what it should be ."
- Work of breathing by Herta Richter: It is based on the idea that the development of your own breath can allow connections to the innermost being.
- Breathing and body therapy after Count Dürckheim: The client is taught to face his behavior patterns and fears in order to allow a fresh start. Here, the body is to be made as " ensouled body ", which forms a unit with the psyche experienced.
- Experiential breath after Ilse Middendorf: It is with the so-called "authorized breath" worked with the idea that between " breath collection and feeling " a mutual interaction is that all at the same time balance between " dedication and attention " a conscious development levels (depending on turning ) of the client is to make it possible.
- The conscious approved respirator - a breathing body - centered, movement and sound work by Erika Kemmann.
- Psychotonic - by Volkmar Glaser, refers to the interaction of mind and tone ( muscle tension ), which affects the respiratory events in a particular way.
- Eutonie by Gerda Alexander: The Eutonie ( = correct voltage ) works with the unconscious passing breath of the client. It is a harmonious balance between tensions arise (hypertension), the solved and relaxations ( hypotension), which are tensioned.
- Holotropic Breathwork by Stanislav Grof: deep breathing ( hyperventilation) to open blockages and cathartic act. Transpersonal experience and connect to the " inner healer " and " higher self " to be possible.
- Integrative Breathing: The breath is used as a way to connect body, mind and spirit. Elements of different schools of respiratory therapy and breath work are specifically tailored to the problem situation and the inner level of development aid seekers. Other psychotherapeutic methods are associated with respiratory experience.
- Intuitive Breathing by Karl Scherer: A breathing method with strong meditative character, which will connect the elements of the biographically influenced the psyche and the body with spiritual and transpersonal areas.
- Mother breath after Reshad Feild: A method that - based on a 7-1 -7- rhythm - it should allow the breather to fully come into the present moment and thus in an increased attention and alertness. Feild approaches are based on various spiritual traditions, including from ancient Egypt, the yoga, the early Christian mysticism, Sufism and to the ideas of the North American Indians.
- Pranayama heard as part of the Yoga of the oldest respiratory therapies. The origins date back to the Upanishads.
- Qigong: ( acquire qi = breath = gong skills) Qigong is based on traditional Chinese medicine. The aim is to harmonize breath, mind and body.
- (Also called respiratory typology ) Terlusollogie: breathing and physical exercises for two different breath types.
- Vocal Breathing: The breathing vowel or vowel singing comes from Indian yoga exercises and was further developed in the West to establish a natural relationship to breath, body and consciousness. It is used in psychotherapy and is next used for voice training, because the voice is "cleared" and strengthened.
- Zen: In the central practice of Zen, Zazen, a certain way of breathing in conjunction with a specific state of mind as a way to enlightenment is seen.