Spectral efficiency
Spectral efficiency, also called bandwidth efficiency, is a term used in telecommunications and refers to the ratio between data transmission rate (in bits / second) and bandwidth of the signal (in Hertz). The spectral efficiency is an important characteristic of digital modulation methods.
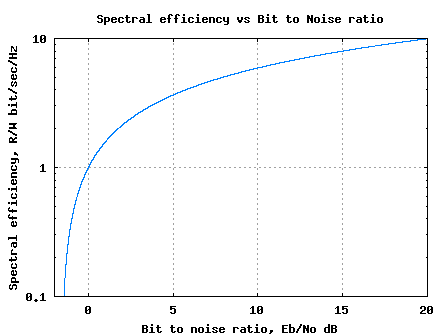
The maximum possible spectral efficiency, in which an error-free transmission is possible in principle, it is limited by the signal -to-noise ratio ( Shannon -Hartley theorem). The more one increases the spectral efficiency for a given signal noise, the more complex forward error correction is required. In spectral efficiencies above the Shannon limit transmission errors can not be avoided even with methods of channel coding; reliable transmission is thus not possible in principle.
At sufficiently high signal -to- interference ratio can take values over 1 bit / s per Hz bandwidth, the spectral efficiency, therefore, such as a modem over a telephone line with a bandwidth of 3500 Hz, a data transfer rate of 33600 bits / s reach. The spectral efficiency in this case is 33600 bit / s / Hz 3500 ≈ 10 bit / s per Hz
Dimension
The unit bit / s / Hz can be cut to bits, which is true, but not intuitive. Hence, often used the unabridged, more understandable form.
Examples
- Measured variable ( Communications Engineering )