Alpha Andromedae
200 L ☉
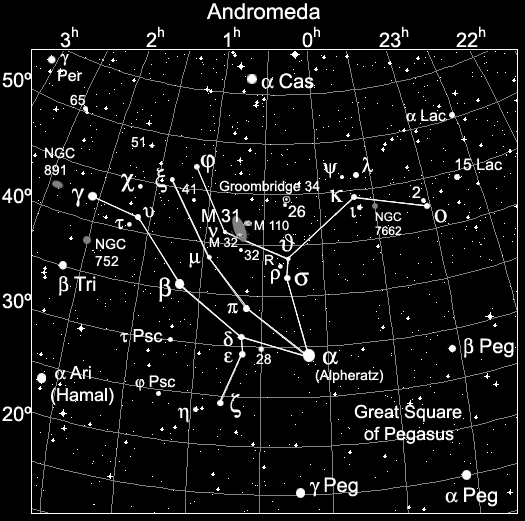
Sirrah, or Alpheratz, is the traditional name of the star α Andromedae ( Alpha Andromedae, short α And). Both proper names go on the Arabic expression سرة الفرس / sirrat al - faras /, Horse Abel ' back. Sirrah is located at the northeastern end of the Pegasus square (autumn square). In some older star charts Sirrah is therefore not counted in the Andromeda, but the Pegasus and as δ Pegasi (Delta Pegasi ) refers.
Location in the sky
The bright star is also part of the Five Star series, which runs from Perseus Andromeda up to Beta Pegasi. Along with its southern neighbor star Algenib ( γ Pegasi ), it marks approximately the " zero meridian " of the sky, the meridian with the right ascension coordinate value = zero.
Stellar Physics
Sirrah has an apparent magnitude of 2.04 mag. The star is a blue supergiant of spectral type B9 and is apparently the brightest representatives of the class of manganese - mercury -star. Therefore show unusual in its spectrum lines of the elements manganese, mercury, gallium and europium. Its surface temperature is about 13,000 Kelvin and its luminosity exceeds that of the sun by 200 times. He belongs to the class of variable stars of type α Canum Venaticorum and its apparent brightness varies with a period of 23.2 hours between the values 2.02 and 2.06 mag.
According to the latest researches and calculations Sirrah has 2.7 times the solar diameter. As a spectroscopic binary, the main component is orbiting with a period of 96.7 days from a companion star. Sirrah is about 100 light years away.






.png)