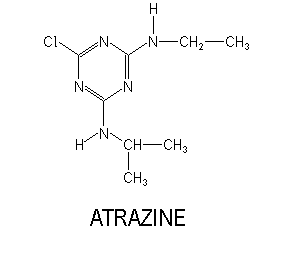
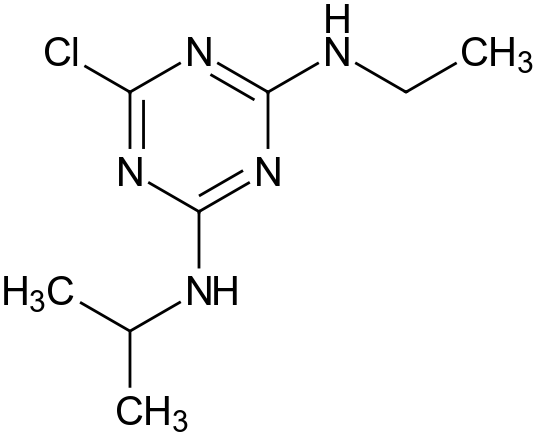
Atrazine
- 6-chloro -N-ethyl -N -isopropyl- 1 ,3,5-triazine -2 ,4 -diamine
- 6 -chloro-4 -ethylamine -2- isopropyl -1 ,3,5 -triazine
White to beige, odorless solid
Fixed
1.23 g · cm -3 ( 22 ° C)
176 ° C.
205 ° C.
Practically insoluble in water ( 33 mg · l-1 at 22 ° C)
Attention
2 mg · m-3 (based on the inhalable fraction )
Template: Infobox chemical / molecular formula search available
Atrazine is the common name of a herbicide from the family of chlorotriazines. Some trade names are Aatrex, Aktikon, Alazine, Atred, Atranex, Atrataf, Atratol, Azinotox, Crisazina, Farmco Atrazine, G - 30027, Gesaprim, Giffex 4L, painter corn, Primatol, Simazat, Weedex, Zeapos and Zeazin.
Properties
The effect of atrazine based on inhibition of photosynthesis of plants. It binds to the quinone QB ( the third member of the electron transport chain in photosystem II by pheophytin and QA), thus interrupting the electron transport. It is broken down only relatively slowly in the environment.
Atrazine is toxic to different organisms. It can even interfere in very low concentrations, the development of male frogs turning them into hermaphrodites. Studies by Hayes and other authors reported that atrazine is not only suspected to reduce testosterone production, but also to stimulate estrogen production and thus to promote the development of breast cancer.
For birds and beneficial insects (eg bees), as well as for soil organisms, the active ingredient is fairly harmless. Atrazine accumulates in the food chain only slightly.
In humans, atrazine has a low acute toxicity. Irritation to skin, eyes and respiratory tract have been observed in isolated cases.
Use
Where the use of atrazine is still allowed, it is used mainly for weed control in corn, but also asparagus, potatoes and tomatoes.
Regulation
Germany
The content of pesticides in groundwater must not exceed 0.1 ug · l -1. Applies after limit exceeded - with a promising recovery plan - an exceptional limit of 3 ug · l -1.
EU
In the European Union, the use of atrazine is banned. The ADI is 0.02 and the Acute Reference Dose 0.1 milligrams per kilogram of body weight per day.
USA
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency recently in 2007 took the view that there was insufficient evidence of damage to amphibians. Since 2010, a comprehensive reassessment is carried out on the basis of published research since 2007. This is due to accumulated atrazine finds together in the drinking water of the Corn Belt.
Resistance
In plants, lambsquarters and annual bluegrass resistance to atrazine and other substances from the class of triazines are known. These are based on a point mutation in the genome of said plastid psbA gene, encoding the binding protein for QB. At position 264 of the peptide an amino acid substitution of glycine by serine took place, whereby the binding affinity of the protein to triazine is greatly reduced.
Historical
On October 31, 1986 reached about 400 liters of atrazine on the effluents of the company Ciba -Geigy in the Rhine, what a day later triggered together with another chemical accident of the Sandoz Group in Basel a fish kill in the Rhine.
Since atrazine and its major metabolite desethyl also reach the groundwater and thus can then be detected in drinking water, the use of atrazine since March 1, 1991, banned in Germany and in Austria since 1995. However it is still widespread in the environment; after the Elbe flood in 2002 for example, it was flooded and could later be demonstrated increased Helgoland, so in mussels and the livers of flounders.