Bamberger rearrangement
The Bamberger rearrangement is a reaction from the field of organic chemistry and, after its discoverer, the German chemist Eugen Bamberger (1857 - 1932) named. The reaction is the synthesis of para- hydroxyaniline derivatives from phenylhydroxyl derivatives in the presence of strong aqueous acids.
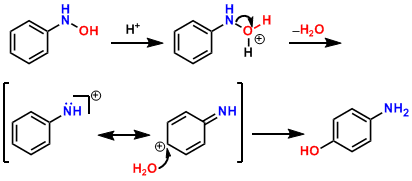
Reaction mechanism
The reaction starts with the reversible protonation of phenylhydroxylamine 1 protonation of the nitrogen atom is preferred, and leads to 2, but is ineffective for the desired reaction. Is the hydroxy oxygen protonated (3) to form a resonance stabilized Nitreniumions 4, water can be removed. Now follows a nucleophilic attack of a water molecule on the aromatic ring. This occurs after rearomatization the product 5