Blastula
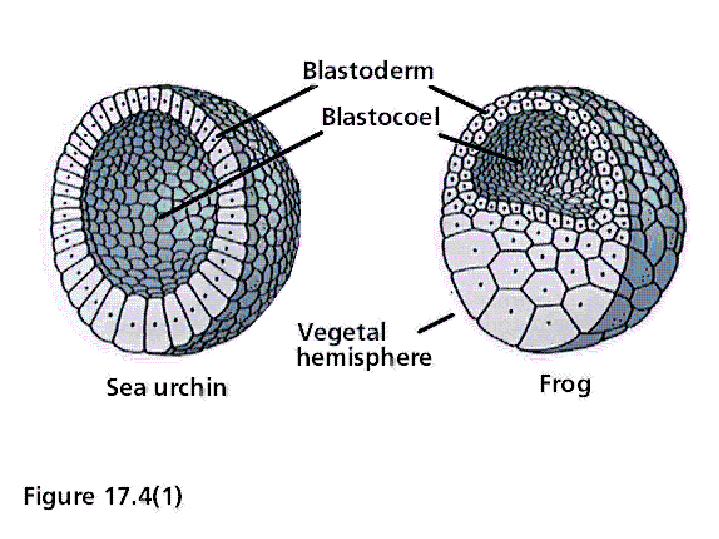
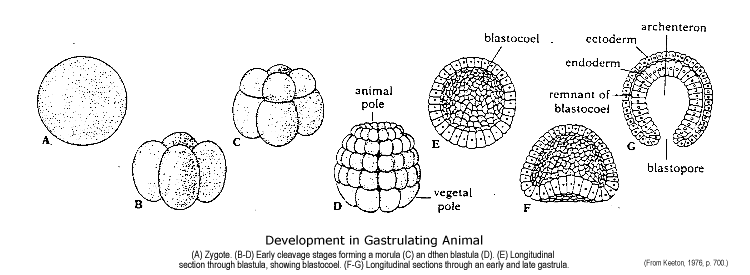
The blastula (from Greek blastos " germ ", " bud ", "sprout " ) is an early embryonic multicellular animals, which follows the morula stage and the segmentation concludes. In a narrower sense is called the blastula only occurring in many animals " bubble nucleation ", which encloses a fluid-filled cavity called the blastocoel. As a result of the formation of the blastula stage, after completion, the Blastulation, developed a multi-layered gastrula whose germ is often irreversible split in two to three germ layers.
Types of the blastula
Coeloblastula
The Coeloblastula or Archiblastula, also called bubble nucleation is often round or egg-shaped and characterized by a more or less centrally or eccentrically located cavity, the blastocoel. It is often regarded as the typical blastula. You can single-layered (for example, in many tissues and lots of hydroids and bryozoans in, water bears, sea cucumbers and acrania ) or multilayer (for example in some scorpions, all sturgeons and amphibians). In the case of a strongly oblate single Coeloblastula is also often spoken of a Placula, for example, in some cnidarians and Wenigborstern. In sea urchins, worms and hedgehogs strings worms which occurs during the Blastulation to premature formation of the middle germ layer ( mesoderm ) can occur.
Sterroblastula
In a Sterroblastula the cavity is missing. Here, again, single-and multilayer blastulas. Examples are flowers animals, acorn worms and spray worms. Bowfin ( Amia genus ) have a complex Sterroblastula with syncytial nuclei.
Discoblastula
A Discoblastula ( " germinal disc " ) is created by animal species with Diskoidalfurchung, for example, in reptiles, birds, and monotremes.
Periblastula
For animal species with a superficial cleavage is called a Periblastula. Since most insects, but also some other animals furrow in this way, the Periblastula is measured by the number of species common blastula type.
Special case of blastocyst
Marsupial and Higher mammals do not form a blastula, but a blastocyst. Here differentiates itself already at this stage at one point of the wall of the hollow sphere a mass of cells from which the embryo is created later ( embryoblast ), while the rest of the embryo ( trophoblast ) formed to assist embryonic organs. The Blastocystenhöhle is not homologous with the blastocoel of Coeloblastula, but corresponds to the early formation of the interior of the yolk sac of reptiles, birds, and monotremes. Therefore, the blastocyst often the blastula is compared.

.jpg/220px-Blastula_(PSF).jpg)