Habitats Directive
Directive 92/43/EEC or Fauna-Flora -Habitat Directive, just Habitats Directive or the Habitats Directive, the European Union (EU ) is a conservation policy, which was adopted unanimously by the then Member States of the EU in 1992. It is used together with the Birds Directive is essentially the implementation of the Bern Convention; one of their main tools is an interconnected network of protected areas, Natura is called 2000. In the years 1994 and 2003 further EU Member States have recognized the policy. The Directive was last amended in 2006 ( with effect from 1 January 2007).
The full German name of the Habitats Directive is Council Directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992 on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora. However, it is almost exclusively used the short name of the Habitats Directive and raised by, fauna ' ( animals), flora ' (plant ) and habitat ' ( living space ) is derived.
- 5.1 Germany 5.1.1 interventions in the conservation area
General
The development of the Habitats Directive at the European Council in 1988 under the German Presidency on 27-28. Decided in June 1988 in Hannover. She joined after four years of discussion in the Member States by a unanimous decision of the European Council and the European Parliament 1992. The Directive has to secure the goal of wildlife species, their habitats and the European networking of these habitats and protect. The cross-linking serves to preserve, ( re) production and development of ecological interactions and promote natural dispersal and recolonization processes. This makes it the central legal instrument of the European Union to implement the commitments made by the Member States also 1992 on the protection of biodiversity ( Convention on Biological Diversity, CBD, Rio 1992).
How the EC Birds Directive of 1979 and the Habitats Directive two main pillars:
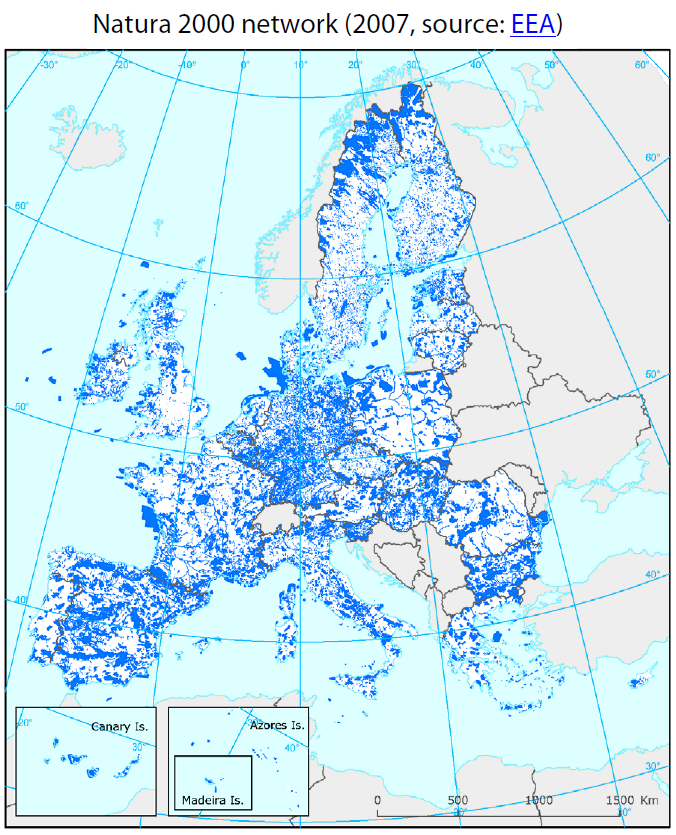
- One of the central pillars of both Directives is the creation of the network of protected areas "Natura 2000". This consists of areas that include a sufficient proportion of the natural habitat types and the habitats of species of Community interest. Thus, the preservation or restoration at a favorable conservation status in their natural habitat types and the habitats of species should be guaranteed in their natural range.
- As habitat types in Annex I typical, not only in Europe threatened with disappearance to the other vegetation types were selected for an on biogeographical regions ( as is approximately the Buchenwald listed even in different forms, the Erlenbruchwald occurring in many parts of the boreal zone, none of habitat type ).
- As Appendix II species were mainly determined such that apply through their claims to the habitat as " umbrella species " for many more occurring in this habitat types (example: Bechstein's bat or Dark burnet - Large Blues ). Of particular importance is priority habitat types and species. These are in danger of disappearance and whose conservation requires the European Community has a special responsibility, because its main application is in Europe (examples: LRT 91D0 * Bog woodland or longicorn ).
- The second pillar are species protection regulations for such endangered species throughout Europe (Annex IV), which can not be protected in the claustrophobic space areas, as they can appear spacious under certain environmental conditions. Some well-known examples are the wildcat ( in forests ) and hamster.
In Annex V species are listed, may be their removal from the nature and use subject to management measures (Annex V species).
Article 8 of the Habitats Directive, Member States have the obligation to investigate the financial resources to implement the Directive and to provide, for example, for land users who may need to implement to achieve the protection objectives farming requirements on their land. This obligation does not come many German Federal States to this day and do not have sufficient funds available so that, especially in agriculture and forestry often uncertainty in the designation of Natura 2000 sites was created.
The Annexes of the Habitats Directive were discussed between 1988 and 1992 and created the basis of the species and habitats of EU Member States. A model was the Bern Convention Council of Europe in 1979. Annexes to be adapted to new scientific evidence, if required, which can be carried about in advance of the accession of new Member States.
Method of Reserve Statement
Special Areas of Conservation under the Habitats Directive are based on " natural habitat types of Community interest" (Annex I of the Habitats Directive ) and " species of Community interest " nominated (Annex II of the Habitats Directive).
Among the Member States proposals for Special Areas of Conservation, Sites of Community Interest Proposed English ( pSCI ) were called, reported to the European Commission, which inspects and evaluates the data. In coordination with the Member States a list of Sites of Community Importance (SCI), Sites of Community Importance ( SCI ) was created. A first-time publication of the list was made in the EU Official Journal in 2004., Member States have since been obliged finally to make these areas within six years as special areas of conservation (SAC ), Special Areas of Conservation (SAC ) under protection.
Process in Germany
- The states compile lists of protected areas. The surfaces to be assembled primarily under the criterion of species and habitat protection and include already existing protected areas under the Federal Nature Conservation Act ( Federal Nature Conservation Act ). In selecting the countries have a nature conservation discretion. However, it may none other than natural technical aspects when choosing to play a role (political expediency, economic and infrastructure interests ).
- The lists of FFH areas report the states to the Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety. Already with the message enjoy the areas declared by the Federal Nature Conservation Act and the conservation laws of the states of temporary protection.
- FFH areas in the ocean are in the territorial waters (up to 12 nautical miles ) are also reported by the countries in the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ, up to max. 200 miles ) is the responsibility of the federal government.
- The Federal Environment Ministry reaches the surface messages on to the EU Commission.
- The European Commission takes the lists after examination on ( " consultation " ) in the Natura 2000 catalog.
Habitat Management Planning
In addition to the collection of inventory data and the testing compatibility measures for the protection and preservation of habitat areas are to create and implement. For this purpose, management plans ( in the directive known as management plans) are developed (Art. 6 § 1 of the Habitats Directive), which allow the implementation of measures for the conservation of protected areas. Furthermore, it can be assessed by the management planning, whether certain measures could have a positive or negative impact. The integrated plan is binding on the conservation authority and allow it clear protection and conservation objectives.
Species protection
Annexes IV and V to Directive species are listed that are to receive special protection outside the designated protected areas (Annex IV) or who are vulnerable to harvest or removal from their wild- occurrence (Appendix V). The reason is that these types effectively be protected would not be through the designation of protected areas, for example because of scattered, at any particular place volatile deposits, special or particularly large-scale habitat requirements, depending on specific land-use practices, etc. The species listed in Annex IV in the implementation of the Directive particular weight. According to the wording may use their " habitats " can not be impaired or destroyed - completely independent of where they are located. The protected through special areas of conservation species have, however, (if a coherent and adequate network of protected areas only reported and thus secured their conservation status ) Outside these protection areas no increased protection. In practice, this is the implementation of construction projects and other interventions on land that the habitats of Annex IV species are considerably more difficult. Destruction of habitats that would threaten a local population are actually only possible if special protection of species compensatory measures (so-called CEF measures ) are performed. In contrast to "normal" compensation measures (due to the impact regulation ) here is a) proof of the success perform necessary (not only forecast! ) B ) are the measures before the intervention / the construction project and must be effective before the procedure.
National
Germany
With the amendment of the Federal Nature Conservation Act ( Federal Nature Conservation Act ) 1998, the Habitats Directive in Section 2 was § § 31 to 36 legally anchored (European Network " Natura 2000 " ) and in species protection in Germany. This happened only after many years of delay and after a ruling by the European Court of Justice ( ECJ) against Germany in December 1997 that forced the then Environment Minister Merkel to act. The species protection provisions of the Federal Nature Conservation Act are still not EU law, most recently Germany was therefore sentenced on 10 January 2006 by the ECJ.
In German law, the Annex IV species " strictly protected " species under the Federal Nature Conservation Act. Compared to the only national strictly protected species, they have a further improvement status. For larger construction projects and other types of interventions, the implementation of a special " species protection test " as a planning standard has become the norm since about 2007. In addition to the Annex IV species is dedicated to this ( protected by the Birds Directive) European bird species.
According to the Federal Agency for Nature Conservation Germany has designated as at 2009/2010 a total of 4,621 FFH areas, which comprise 9.3% of the terrestrial and 37.4% of the marine area of Germany.
Interventions in the conservation area
When intervening in the FFH area now has a previously
- Be carried out risk assessment process ( VP ) (§ 34 para 1, 2 Federal Nature Conservation Act ). Here is considered a fundamental prohibition of deterioration. This impact assessment is carried out independently of any possible additional required Environmental Impact Assessment ( EIA) under the EIA Act. Also the processing of the impact regulation under the Federal Nature Conservation Act and its implementation in the national legislation is carried out independently.
- Upstream of the impact assessment is a preliminary test in which it is checked whether the possibility of a substantial impairment of a project on the conservation area can arise, compatibility assessment ( VA). Basically it does not matter whether the project takes place directly in the field or running outside its influence on the conservation area. Depending on the result is an impact assessment carried out or not. Can be a significant impairment demonstrably not exclude, must be a VP.
- If the impact assessment that the project could have adverse influence of an FFH area in its objectives for the conservation or protection of the elements fundamentally, it is first permitted.
- In assessing the cumulative effect is to consider a number of smaller intervention. In doubt, the last, the materiality -border intervention is inadmissible, even if it would, in itself remain below this threshold.
- This inadmissibility of the project can only be overcome if in the context of an alternative test ( § 34 para 3 No 2 Federal Nature Conservation Act ) can be demonstrated that there is no project and location alternative out there that can be realized under reasonable conditions and the area or not less affect than the actual project.
- In addition, it must be shown as an additional admission requirement is an overriding public interest. This must be in individual cases higher outweigh the public interest in the protection of the affected area. If by the engagement known as a priority habitat in Annex I or a priority species affected by Annex II, already registered FFH areas of the EU Commission's approval is required.
- Is the procedure under the Federal Nature Conservation Act in a Natura 2000 area permitted, a balance should be paid for it.