Zellweger syndrome
Zellweger syndrome
Zellweger syndrome, also known under the synonym cerebral hepatic - renal syndrome or cerebro- hepato - renal syndrome, is a rare genetic autosomal recessive inherited peroxisomal metabolic disorder on the basis of a congenital genetic mutation. It is fatal.
The disease was first described in 1964 by the U.S. doctor Swiss descent Hans Ulrich Zellweger in twin pairs.
Epidemiology
Zellweger syndrome is one of the rare hereditary disease and can be diagnosed in an estimated 1 in 100,000 newborns. Girls and boys are equally affected.
Since 1964, over 100 cases have been documented, occurring both sporadically and in a sibship.
Cause
In the first place, the syndrome is the cause in the absence of peroxisomes and peroxisomal biogenesis by impaired, which is accompanied by a corresponding loss of the liver, kidney and other organ functions. Furthermore, there is a loss of activity of several peroxisomal enzymes, which affects various metabolic functions.
From real Zellweger Syndrome pseudo - Zellweger syndrome is distinguished. In this there is a loss of activity of the acyl- CoA oxidase, a peroxisomal enzyme before.
Zellweger syndrome is due to mutations in the genes necessary for the formation of peroxisomes. These include serine -lysine -leucine - receptor Pex5 and more usually, the gene for the ATPase Pex1.
Are caused by mutations in PEX1 or PEX5 or other genes for Peroxisomenentstehung before, so is the enzyme responsible for the cleavage of hydrogen peroxide - a cytotoxin - is necessary, catalase, no longer introduced into the peroxisome.
In peroxisomes in addition to the catalase reaction, various other biochemical reactions take place that have to do with the degradation and modification of fatty acids. Thus, for example, fatty acids having a chain length of 22 carbon atoms degraded solely in the peroxisomes. Also, bile acids are completed in peroxisomes. However, what is the essential role of peroxisomes whose failure causes the symptoms of Zellweger syndrome, is still not released.
Symptoms
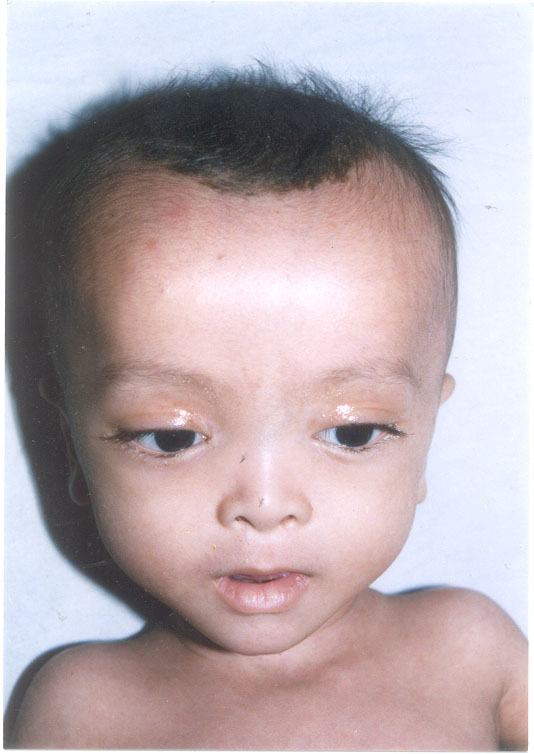
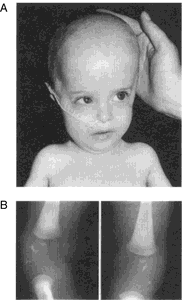
Children with Zellweger syndrome often come before the expected date of birth as born prematurely. Newborns have a combination of features, not all features are present in all children and all children in the same strong expression. The most common symptoms include:
- Special features of the head and face: vertical overdevelopment of the head ( Skaphocephalus / long skull)
- Lack of clearly defined ( hypoplastic ) nose
- Relatively flat and rectangular -looking face
- High, domed forehead
- Comparatively low in the head -set ears
- In newborn children not yet ossified comparatively large area of the skull ( fontanel )
- Reserve of the lower jaw and the teeth due to a growth disorder ( mandibular retrognathia )
- Velum column
- Remarkably little visible movements of the facial surface (reduced facial expression )
- Special features of the eyes: relatively long eye relief ( hypertelorism )
- Flat edges of the bony eye socket (orbit )
- Corneal opacity
- Lens opacity
- Regression of the optic nerve, leading to loss of visual acuity, visual field defects and extensive blindness ( optic atrophy )
- Brushfield spots ( mottling of the iris )
- Epicanthus medialis (small fold of skin at the inner corners of eyes )
- Slanted palpebral fissures
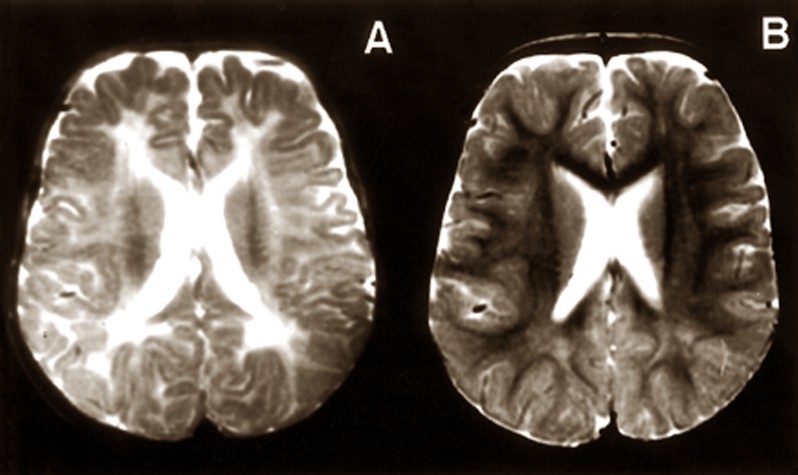
- Special features of the brain cerebral cysts ( cysts in the brain, subependymal pseudocysts )
- Decreased expression of brain convolutions ( microgyria ) or Windungslosigkeit ( agyria )
- Enlargement of the lateral ventricles in the brain
- Special features of the internal organs Underdevelopment of the lungs ( pulmonary hypoplasia )
- Special features of the biliary tract
- Special features of the kidneys ( multicystic renal dysplasia )
- Special features of the liver ( hepatic insufficiency, severe liver enlargement / hepatomegaly, siderosis / iron storage disorder)
- Special features of the spleen ( siderosis / iron storage disorder)
- Heart defects, especially ventricular septal defects
- Thymusdysplasie
- Other features severe cognitive disability
- Strong Psychomotor retardation
- Maldevelopment of the external genitalia in girls
- Disturbance of the formation of bone tissue ( ossification )
- Shrill -sounding wines
- Marked decrease in muscle tone ( hypotonia ) with limitation of joint mobility
- Reflection reduction ( hyporeflexia ) or absence of reflexes ( areflexia )
- Epilepsy
- Difficulty in breathing ( dyspnea leading to life- threatening respiratory arrest)
- Short stature ( below-average growth in length )
- Simian crease
- Tall, broad thumbs
- Slight bending of the little finger and / or the ring finger in the direction of each of right side lying next to the finger ( camptodactyly )
- Special features of the epiphyses ( the stem ends of long bones ), particularly selective calcifications in corresponding areas of the knee and hip joints
- Reduced due to lack of propanoyl -CoA acyl transferase, and the accumulation of bile salts pristanic
Diagnosis
On a Zellweger syndrome in a baby the special features of the face, the hypotonia and the cysts in the brain and the kidneys can draw particular attention.
A diagnosis can be made by the detection of changes in the fatty acids in serum ( concentration of " Überlangkettigen " fatty acids) and plasmalogens. Pipecolic acid is another hint. In fibroblasts and hepatocytes, the absence of peroxisomes can be detected. The diagnosis should be verified by the identification of the genetic modification (mutation).
In the context of prenatal diagnosis, so prenatal diagnosis, can the Zellweger syndrome in which a chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis subsequent investigation of the unborn child of the cells on the basis of an exceptionally high content of long-chain fatty acids, decreased plasmalogen concentration and low activity of the acyl- CoA: DHAP - transferase be diagnosed. With appropriate microscopic examinations no peroxisomes are visible.
The differential diagnoses pseudo - Zellweger syndrome, 3 - oxoacyl -CoA thiolase deficiency, Hyperpipecolazidämie, Chondrodystrophia punctata, Refsum's syndrome, Smith - Lemli -Opitz syndrome and other Peroxisomopathien should be taken into consideration before the Zellweger syndrome definitively diagnosed will.
It is in principle possible that the syndrome is not recognized as such, but one of the possible differential diagnoses, particularly the pseudo - Zellweger syndrome or Hyperpipecolazidämie, is assigned as a clear separation is not always possible.
Therapy
So far, no causative healing treatment and therapy options are known. The Zellweger syndrome lethal disease, which means that children are not viable in the long term with this feature. They usually die during the first months after birth.