Aspergillus terreus
Aspergillus terreus
Aspergillus terreus is a fungus of the genus Aspergillus, which can occur worldwide as saprophytes and cause poisoning or allergies.
Features
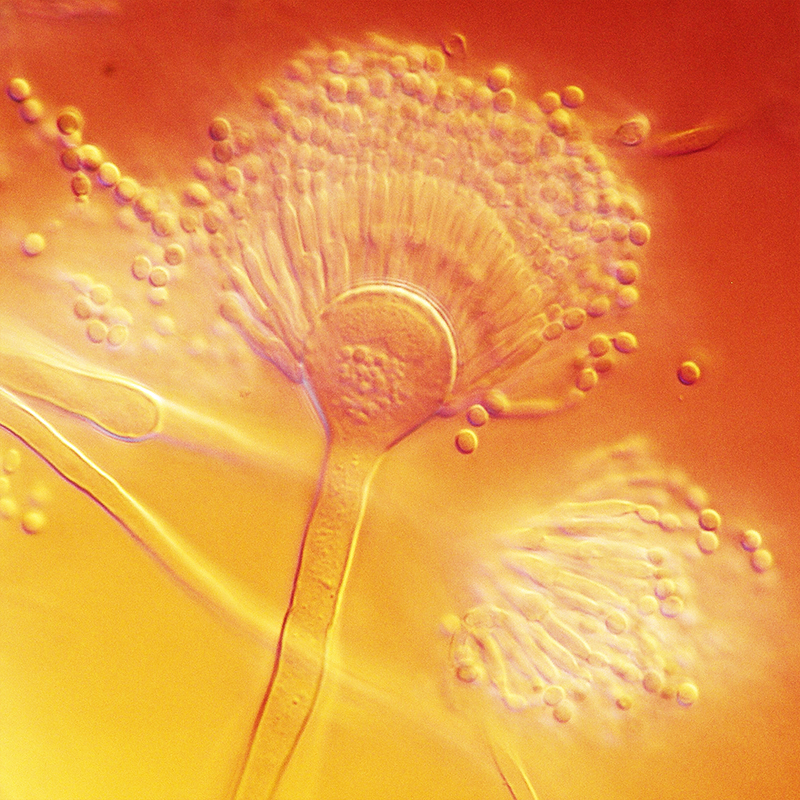
Aspergillus terreus is on Czapek agar pink - cinnamon brown to deep brown aged colonies that grow mostly velvety. However, some strains grow significantly flaky or form aerial hyphae from. On the underside of the colony, the colonies are pale or light yellow to deep brown. Smell is not available in many tribes, in some, a volatile odor is determine at least. The slightly flexible conidiophores are 5-8 microns wide and 250 microns long with a smooth up to 1 micron thick cell wall and are both septate and unseptiert. They have an enlarged spherical apex of 12 to 18 microns, sometimes up to 25 microns is large. For this grow densely packed phialides in two rows (primary and secondary phialides ). The primary 2 to 2.5 microns wide and 7-9 microns long, the secondary are 2-2.5 microns wide and 5-7 μ long. At maturity, these heads are up to 500 microns long and 50 microns wide. The smooth conidia are slightly elliptical to spherical and are of 2.2 to 2.5 times to 3 microns in size and are formed into long contiguous chains. Perithecia were not found. The optimum growth temperature is 37 ° C. The fungus can liquefy gelatin.
Artabgrenzung
Aspergillus terreus is like colonies such as Aspergillus fumigatus or Aspergillus nidulans. However, they are green in contrast to Aspergillus terreus. Aspergillus fumigatus also has only single row sterigmata. Aspergillus rehmii also has double row sterigmata, but is yellow.
Habitat
Aspergillus terreus is commonly found in soil and decaying plant material. The spores can survive the digestive tract unharmed. Feeding trials of spores in rabbits were lethal for this, however.
Importance
Aspergillus terreus can cause a serious aspergillosis whose infection often has a mortality rate of 100 %. It is resistant to amphotericin B.
On the other hand, Aspergillus terreus is used for the recovery of lovastatin, a statin, which is used for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. The world market for statins is estimated at more than $ 12 billion annually. Aspergillus terreus produces numerous secondary metabolites, such as patulin, citrinin and economically important enzymes such as xylanase.
The Industrial Biotechnology, Aspergillus terreus is used primarily for the production of itaconic acid, with the commercial use in 1952 for the first time launched by Pfizer in the United States and later in the UK.
System
Aspergillus terreus was scientifically described in 1918 by Charles Thom for the first time.









_1024X768.jpg)