Assyrian Neo-Aramaic
Spoken in
- Afro-Asiatic languages Semitic languages West Semitic languages Aramaic Ostaramäisch Nordostaramäisch Assyrian - Neuaramäisch
Aii
The Assyrian- neuaramäische dialect ( Aramaic: ܐ ܬ ܘ ܪ ܝ ܐ Ātûrāyâ, ܣ ܘ ܪ ܝ ܬ suret inter alia, also Nestorian neuaramäisch; russian earlier ajsorskij, hence the name Aisor, today assirijskij ) is a nordostaramäischer dialect, which has a total of about 200,000 speakers. Original distribution areas are Iraq ( 30,000 speakers), Syria (about 30,000 speakers) and Iran (about 15,000 speakers). Smaller groups of speakers can be found next in Transcaucasia, namely in Georgia and Armenia, as well as Russia and the Ukraine. Other groups of speakers migrated since the Second World War to Western and Central Europe, North America and Australia.
The Assyrian- neuaramäische dialect is close to the Chaldean neuaramäischen dialect and some smaller nordostaramäischen dialects. With the Assyrian dialect of Akkadian ancient Near Eastern language, it has no direct connection, but both belong to the Semitic languages.
The speakers of this dialect are mainly East Syrian Christians.
Font
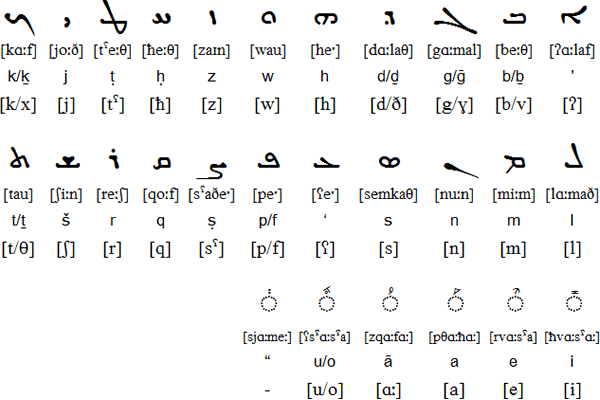
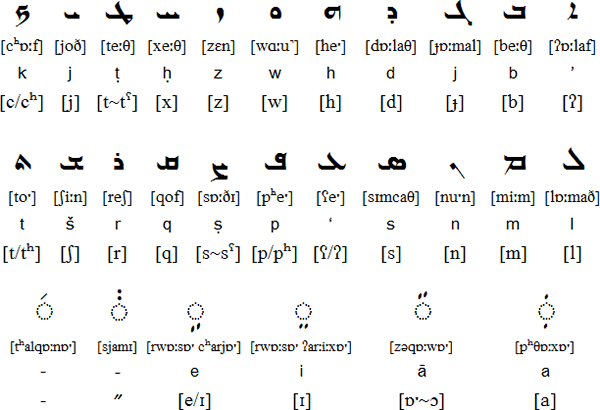
The Assyrian - Neuaramäische is written in three scripts Estrangelo, Serto and Nestorian (see Syriac alphabet ), the dialect of Urmia (Iran) will be used.
In the 20s and 30s of the 20th century, attempts were made on the territory of the Soviet Union to verschriften the language using the Cyrillic or Latin alphabet.