Bandarban District
The district Bandarban ( Bengali: বান্দরবান জেলা, Bāndarabān Jela ) is an administrative unit in southeastern Bangladesh, which is within the Division Chittagong. The capital lies in the northern part of the district is also called Bandarban.
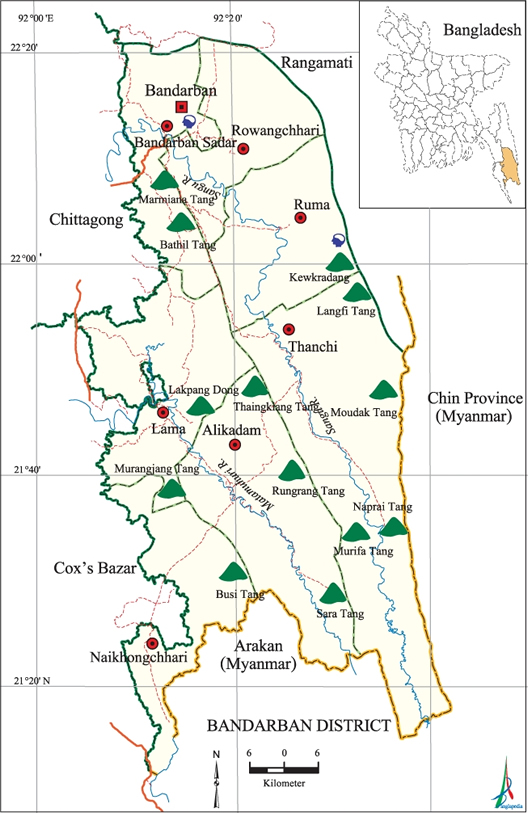
The 4479 km ² large district is bordered to the north and east to the neighboring district of Rangamati and the provinces of Rakhine and Chin of the eastern neighboring country Myanmar, on the south by the river Naf and the west by the national districts Chittagong and Cox 's Bazar.
The main rivers of the dominated to two-thirds of forests and mountains district are the Bakkhali, Matamuhuri and the Shankha ( Sangu ). The four main mountains are Bandarbans Meranja, Wailatong, Tambang and Politai. The district is part of the mountainous region of Chittagong Hill Tracts.
The 1983 created administrative district is divided into the seven so-called Upazilas: Bandarban Sadar, Rowangchhari, Ruma, Thanchi, llama, Alikadam and Naikhoncchari. Within this administrative subdivision, there is a self-governing city ( municipality ), 32 Union Parishads (village councils) and 1482 villages.
Marma, Murong, Tripuri, Bawm, Tanchangya, Chakma, Chak, Khyang, Khumi, Lushei and Pankho: In the ethnically highly diverse mountain district the peoples of life. To live in Bandarban in contrast to the rest of the Muslim-dominated country, a significant number of Buddhists who represent at least one third of the population there.
Agricultural main products are rice, mustard seed, cotton, tobacco and vegetables. As the most common fruits are banana, pineapple, jackfruit, oranges and papayas. The main export products are accordingly banana, jack fruit, cotton and bamboo.





.jpg)



