BASE (search engine)
BASE ( Bielefeld Academic Search Engine ) is a search engine for scientific, multidisciplinary Internet sources. It is operated by Bielefeld University Library with the search engine technology of open source software Solr / Lucene. BASE will be further developed as a strategic project continuously.
- 3.1 Scientific Internet sources
- 3.2 Selection of sources and transparency
- 3.3 topicality and scope
- 3.4 Country coverage and Languages
- 3.5 Rights-managed sources
- 4.1 User Interface and Navigation
- 4.2 Search functionality
- 4.3 Browsing
- 4.4 BASE Lab
- 5.1 Search Engine Technology
- 5.2 Integration of data sources
- 5.3 Interfaces to third-party
Target Group and Objectives
The offer of BASE is aimed primarily at researchers in universities and research institutions and to students. With the development of BASE University Library aims to build a reliable, high-quality search services for research and teaching with the help of search engine technology.
BASE would like to give access to the contents of scientific repositories that are provided as part of the Open Access movement free of charge via the Open Archives Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting (OAI -PMH ) is available. The search engine is registered as official OAI service provider and has been involved in the EU project Digital Repository Infrastructure Vision for European Research (DRIVER ), which was completed in 2009.
Because of the intellectual selection of sources BASE has the ambition to provide professionally qualified information in connection with extensive and high-quality metadata and thereby be distinguished from commercial search engines.
History of development
Chronology
Content
Scientific Internet sources
The contents of BASE are multidisciplinary. Are evaluated exclusively scientific sources. BASE has the ambition to open up "Internet sources of the ' Invisible Web', which are not indexed in commercial search engines, or perish in their large numbers of hits ." BASE offers:
- OAI metadata The search engine contains primarily metadata from repositories that provide their content on the Open Archives Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting (OAI -PMH ). In addition to the OAI metadata selected web sources and local data holdings of the library are indexed.
- Data from local repositories at the University of Bielefeld
- Selected sites (eg, sites of scientific organizations)
Selection of sources and transparency
All sources are searched intellectually selected and tested. A source directory makes the selection transparent.
Timeliness and scope
The Index is updated daily, the contents of individual documents servers are added weekly.
Currently, 50,063,294 documents from 2690 sources via BASE are searchable. The number of documents and sources has grown steadily for the new production and the index is expanded. Thus, repository operators, which are not listed in the bibliography, are asked to contact the BASE team.
Country coverage and Languages
Sources by country
Overall, sources are from 88 countries in the index. The 20 countries with the highest indexed sources are:
Sources by continent
The European countries are the most common, followed by North America, Asia, South America, Australia and Africa.
All details: Stand August 27, 2013
Documents by language
Sort by languages , the following picture.
About 1 /3 of all sources are not associated with language.
Rights-managed sources
The ability to search only free or only licensed sources will no longer be offered in BASE, as more and more repositories offer via the Open Archives Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting (OAI -PMH ) and metadata to not freely accessible documents and BASE therefore the free access can not be guaranteed. This means that the metadata of the documents are displayed, but they are in electronic full- text is not necessarily accessible. If the document is managed, BASE refers to the fact that the license check is undertaken solely by the providers and information seekers should contact their institution or university in order to obtain access. Thus, BASE has not only according to Open Access offers.
Functions
User Interface and Navigation
The barrier-free user interface of BASE is designed simply and clearly. The search interface is English, French, Polish and Spanish offered in German. Information about BASE are available in German and English.
The home page allows you to search in the BASE - index (default search). From here takes place the transition to continued operation and research areas of BASE: Advanced Search, Help, browsing and search history as well as to mobile version. The options are in a title bar, which is made uniform for all search pages that can be so easily switch between the functions. Below the search reaches you, inter alia, on the pages About BASE ( general information about the research portal ), the BASE- blog, the Twitter channel and the BASE Lab ( developments ).
Search functionality
Standard Search consciousness oriented to the success of Google, BASE presented to the user for the access point the default search with just a simple search slot, which is available by default for the free text search. Using a stated in the help syntax, it is possible to limit the search of individual terms on individual metadata fields. When entering the search terms wildcards can be used for right truncation.
In addition, the standard search provides the option of automatic extension of search terms to other forms of words ( lemmatization ).
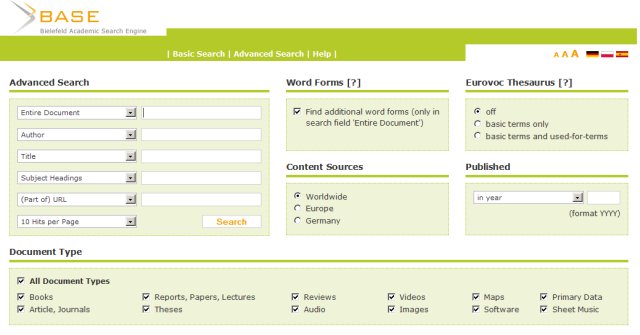
Advanced Search The Advanced Search opens by default the ability to specifically enter the search terms for the following metadata fields: Whole document, author, title, keywords, and ( part of) URL. The search throughout the document corresponds to the standard search. The five individual metadata fields can be combined. You will be automatically linked with the Boolean operator AND. Within a search box that searches through various Boolean operators through a dedicated, documented in the help syntax can be combined.
There is also the option of narrowing down the search for the origin of the sources (certain countries or continents), to specific publication years or periods, and on certain types of documents (eg books, articles, dissertations, videos). Likewise, the number of items displayed in the hit list titles are limited ( 10, 20, 30, 50 or 100).
View results The search results are displayed in a list, which by default is sorted by relevance. The determination of the relevance, according to various criteria, for example, it plays a role in whether the search term appears in the title, or elsewhere. The default ranking, however, can be changed and a custom sort by author, title or year be selected optionally in ascending or descending. Besides the number of hits and the query time is displayed.
The single search result contains - if available - extensive, qualified metadata ( such as next to the title and author and keywords, publisher, source, language, Abstract, URL). Integrated in the hit list is the
- Link to the original document (metadata or electronic full text )
- Link to a new search for the author,
- Link to data suppliers,
- Link to a search on Google Scholar ( by searching for the title on Google Scholar can with him linked citations or different versions of the work are found),
- Link to export via e -mail and in reference management programs,
- Link to add as a favorite in the personal profile ( with login ).
Is the hit too large, it can on author, subject, year of publication, source, language, document type or access ( Open Access / unknown) are limited. A time can be selected only one option from the drop-down menus.
In addition, the queries in the current session in a search history will be displayed, which can be re- sold, respectively. With a personal login search queries can also be stored permanently. In addition, searches can be subscribed to as an RSS or Atom feed, the search results can be sent or stored by e -mail. A personal login is also necessary for the latter.
From the hit list can be triggered by changing the current search query directly a new search.
Browsing
In addition to finding BASE also offers a browsing of Dewey Decimal Classification ( DDC) and by document type. The DDC classification of the documents comes about in two ways: On the one already from several data sources DDC numbers are assigned, which are transferred directly into the browsing. On the other hand, documents within BASE will automatically nachklassifiziert. The technique used for this purpose has been developed within the DFG -funded project " Automatic enhancement of OAI metadata ".
BASE Lab
BASE offers BASE Lab on a public test area can be tested in the new features. Currently, the following functions are tested:
- Use computational method for the automatic classification of OAI metadata within the DFG - project " Automated enhancement of OAI metadata using computational methods and development of services for content- oriented networking of repositories ". More information about the project.
- Building a service for providing aggregated and normalized OAI metadata
- Expansion of the labeling of Open Access documents
Technical Basics
Search engine technology
Technical basis is the search engine technology and Vufind Solr. It enables
- The use of a linguistic approach to the optimization of search queries ( eg, lemmatization, decompounding, permutations ) Through automatic speech recognition and generation of dictionaries search terms to other word forms (plural, genitive ) to be expanded.
- Relevance ranking of search results The relevance is determined by an algorithm contained in the software
- Subsequent narrowing down the number of hits according to certain criteria ( author, subject, year of publication, source, language and document type).
Integration of data sources
The data will be transmitted through different interfaces in the search engine, namely
- OAI harvesting Metadata for selected OAI repositories are integrated via the Open Archives Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting (OAI -PMH ).
- Web crawlers Scientific content from Web pages are collected through an integrated web crawlers. The full-text data collected here are analyzed contained metadata down.
Interfaces to third-party
BASE allows through links in the hit lists the direct search for individual titles in Google Scholar. Does the user BASE spot in a library, links may result in Google's search results for offered by the library full text. This sets the configuration advance from the library.
Similar offers
A similar offer as BASE offer the scientific search engine Scirus from Elsevier Publishing and OAIster at the University of Michigan. BASE limited to scientific university server as opposed to Scirus, the many journal articles from publishers. OAIster uses the same field as BASE is in scope but much smaller and provides this via OCLC and WorldCat are available.
Involvement in specialized portals
The OAI service provider BASE is involved in the meta-search of several German trade portals. Fachportal paedagogik.de, German on the net, ilissAfrica, vifabio and Virtual Library media, stage, film- bind either the full BASE index or filter your search for a variety of repositories, which fit to the tray. Since not only classic Hochschulschriftenserver, but also platforms with digitization of photos, maps and other source materials are geharvestet, BASE also opens the way toward primary research data and virtual research environments.