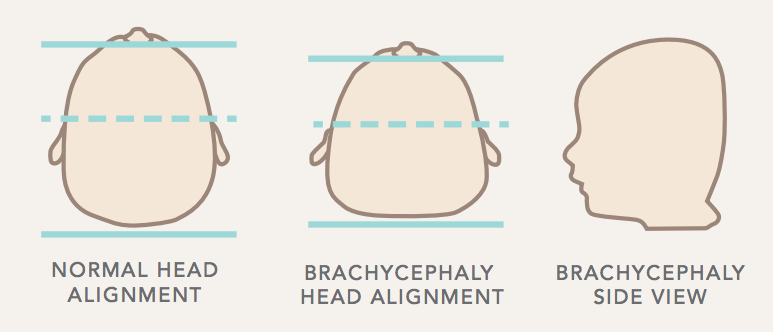
Brachycephaly
Brachycephaly (also: brachycephaly, of gr βραχύς brachys, short ' and κεφαλή kephale, head ') means Kurzköpfigkeit or Rundköpfigkeit. It is a congenital, hereditary deformation of the skull, which leads to various health problems. Among the domestic animals are especially dogs, partly affected cats.
- 5.1 Germany
- 5.2 Austria
- 7.1 Literature
- 7.2 Notes and references
- 7.3 External links
Definition
The definition of a skull as brachycephalic done according to several criteria. On one hand, one uses the external appearance of an entire race and refers to short and wide skull as brachycephalic. On the other hand, skull measurements are relied upon to classify a single animal as brachycephalic. This can lead to mean that some are not as brachycephalic breeds applicable very well to find dogs with brachycephalem skull. These include, for example, the Norwich Terrier. This general dilemma can not be solved, especially as the permanent and breeding caused change in the shape of the skull is rapid.
The famous skull measurements are:
- Ratio width of the skull to skull length of 0.81 or higher
- Ratio of cranium to face skull greater than 1.6
- Kraniofazialwinkel ( CFA) between 9 ° and 14 °
- Relation to craniofacial cranium smaller 1.25 (S- index)
The first two indices are collected on carcasses. The CFA and the S- index searcher uses x-ray images, which has the great advantage that the measurements can be carried out in living dogs. The Kraniofazialwinkel is limited by the tip of the snout, the cranial base and the center of the orbit angle. ( Brachycephalic = short head; mesocephal = average long head, doolichocephal = long head) Here, however, massive overlaps in the three skull shapes were found, so that the S- index is considered as reference for its clinical application, at least in Switzerland.
Health Consequences
Brachycephales syndrome
Brachycephaly can lead to problems of the upper airways, which are collectively referred to as brachycephales syndrome or brachycephalic syndrome. It is characterized by a strong obstruction of breathing and impaired thermoregulation.
Pathogenesis
Cause of the narrowing of the upper airways is mainly an inhibition of longitudinal growth of the facial skeleton.
Due to the voluminous extent of the cartilage of the nasal wing (especially the cartilage nasi lateralis dorsalis) and a reduced mobility of the nose wing, there is a narrowing of the nostrils. The nasal cavity of the growing dog normally extends in the length and the birth of underdeveloped nasal turbinates grow toward each other, but make their growth before the one they encrusting mucosal layers touch each other. In brachycephalic dogs this growth inhibition is omitted - there is a relative conchae hypertrophy ( " turbinate overgrowth "). In addition, the nasal turbinates grow as aberrant conchae about a possible for the size of the nasal cavity dimension. A distinction is aberrant rostral nasal turbinates (before the alar plica located ), narrow the front portions of the middle and lower nasal passage, and aberrant caudal nasal turbinates, narrowing the transition to the nasopharynx ( meatus nasopharyngeus ). In addition, the blades of the nasal turbinates in brachycephalic dogs are much thicker than other dogs. The result is that hardly any air can flow through the nose, which is a serious problem for an obligate nose breathers.
The soft palate brachycephaler dog is elongated and thickened. This leads to a narrowing of the nasopharynx and in combination with the relatively large tongue ( macroglossia relative ) also oropharynx.
In the area of the larynx also occur pathological changes, especially when pug. Here, the laryngeal skeleton is unstable, especially the arytenoid cartilage and the epiglottis, so that the risk of laryngeal collapse exists. In addition, the mucous membrane is usually in excess corniculates formed in the region of the processus and swollen, so that it is drawn during inhalation through the glottis and they moved partially.
In the area of the trachea and large bronchi appear race-specific malformations. The cartilage rings of the trachea are so they tend the pug soft ( tracheomalacia ), for tracheal collapse. In contrast, the cartilage rings of the French Bulldog may be small, but usually sufficiently stiff ( hypoplastic trachea). These changes are also continued on the large bronchi.
Clinical picture
A typical symptom of brachycephalic syndrome is a noisy, usually inspiratory stressed breathing in conjunction with signs of respiratory distress. On clinical examination, can be found as characteristic findings narrowed nostrils and nasal cavities, an extended and thickened soft palate, pharynx shortened and changes in the larynx. In addition, the tonsils can be drawn into the interior of the respiratory tract by inhalation when the negative pressure becomes too large. This can cause breathing problems, choking, fainting, but at least gasping breath noise and snoring sounds. The reduced ability to respond Panting brachycephalic dogs more sensitive to heat than their undeformed counterparts.
Possible complications of brachycephalic syndrome are edema of the epiglottis, collapse of the larynx, invagination of the lateral laryngeal pockets inside, tracheal collapse, inflammation, and / or prolapse of the adenoids, bronchitis and heart failure due to insufficient oxygenation of the blood.
Often an increased susceptibility to heat can be observed. Since the nasal turbinates and the lateral nasal gland play an important role in heat dissipation, brachycephalic dogs are often very sensitive to warm ambient temperatures.
Therapy
The treatment of brachycephalic syndrome can be done by conservative or surgical measures, with a weight reduction and conservative treatment with corticosteroids provides only mild cases likely to succeed.
The surgical treatment consists of resection of the airway constricting tissue ( nostril expansion, Vestibuloplastie, laser-assisted turbinectomy, Gaumensegelresektion, tonsillectomy, etc.), thereby allowing a freer breathing.
Other health problems
The proportional enlargement of the head in conjunction with the round head shape mechanically leads to an increased risk of dystocia. Even with a cesarean section, the survival rate of brachycephalic puppies compared to anatomically normal dogs is reduced. Brachycephalic breeds are also disproportionately affected by brain tumors and hydrocephalus. This is particularly marked predisposition is in breeds in which a chondrodysplasia in addition to brachycephaly available. The strong deviation from the normal head shape also leads to an anatomical reorganization of the brain. Brachycephalic dwarf breeds are commonly affected by persistent next to adulthood fontanelles, which is due to the lack of protection of the brain in the cranial cavity, an additional risk of injury.
Brachycephaly through the shortening of the upper jaw ( brachygnathia superior) often a pronounced underbite, which is in some brachycephalic breeds also specifically required by the standard. This can in some cases lead to poor dentition function.
At the extremely round-headed breeds ( eg Pug) protruding, partly enlarged eyes are also observed, resulting in frequent injuries of the cornea. There is also the risk of Augapfelvorfalls. This symptom complex is occasionally referred to as ocular Brachycephalensyndrom.
Genetics and breeding hygiene
Brachycephaly is a complex of various anatomical features that are inherited polygenic. For animal welfare considerations extremely brachycephalic animals should be excluded from breeding. In particular, the extreme Rundköpfigkeit in combination with a pronounced shortening of the facial bones is to fight for breeding, which is possible on setting limits and based on this index selection and genetic evaluation.
Breeding attempts to combat Brachycephaly and brachycephalem syndrome, for example, the Continental Bulldog and the Olde English Bulldog.
Affected breeds
The following breeds are affected by the occurrence of brachycephaly and the consequences due to the breed development in recent decades:
- Canine Maltese
- Pug
- English Bulldog
- French Bulldog
- Boston Terrier
- Boxer
- Shih -Tzu
- Pekinese
- Chihuahua
- King Charles Spaniel
- Belgian Zwerggriffons ( Griffon Belge, Griffon Bruxellois, Petit Brabançon )
- Yorkshire Terrier
- Miniature Pinscher
- Cats Persian cat
- Exotic Shorthair
- British Shorthair
A brachycephalic syndrome like disease in which a brachycephalic breed of dog is not clearly described in the Norwich Terrier, whose skull has a limited brachycephalic anatomy.
Legal situation
Germany
Strong manifestations of Brachycephaly apply, according to a report by the Federal Ministry of Consumer Protection, Food and Agriculture as prohibited torture breeding. In the opinion of the breeding associations studies of affected animals, breed restrictions and revised breed standards are recommended.
In § 11b of the Animal Welfare Act, which regulates the prohibition of torture breed, is set out below:
"It is forbidden to breed vertebrates [ ... ] if it can be expected that in the offspring [... ] hereditary body parts or organs for the species-specific use are missing or unfit or altered and thus pain, suffering or damage. "
Austria
The Federal Law on the Protection of Animals § 5 breathlessness is known as one of the health effects of torture breeding, so that in consequence the breed, but also import, acquisition, transfer or issuing of similar animals are prohibited. According to § 38 are violations of § 5 with a fine of up to 7,500 euros to punish up to 15,000 euros in case of recurrence. However, there is according to § 44 (17 ), a transition period in which documented by written breed measures to ensure compliance with the provision until January 1, 2018, there is no infringement.
Further use of the term
The term brachycephaly can be found in the literature ( Anthropology ) of the 19th century. There the division of human races ( quote from ) had been attempted by means of measurement of the skull.
In human medicine, there is the term used to describe Brachycephaly (congenital ) growth disorders such as achondroplasia.