Brushite
- Epiglaubit
- Ca [ PO3 (OH)] · 2H2O
- CaH [ PO4 ] · 2H2O
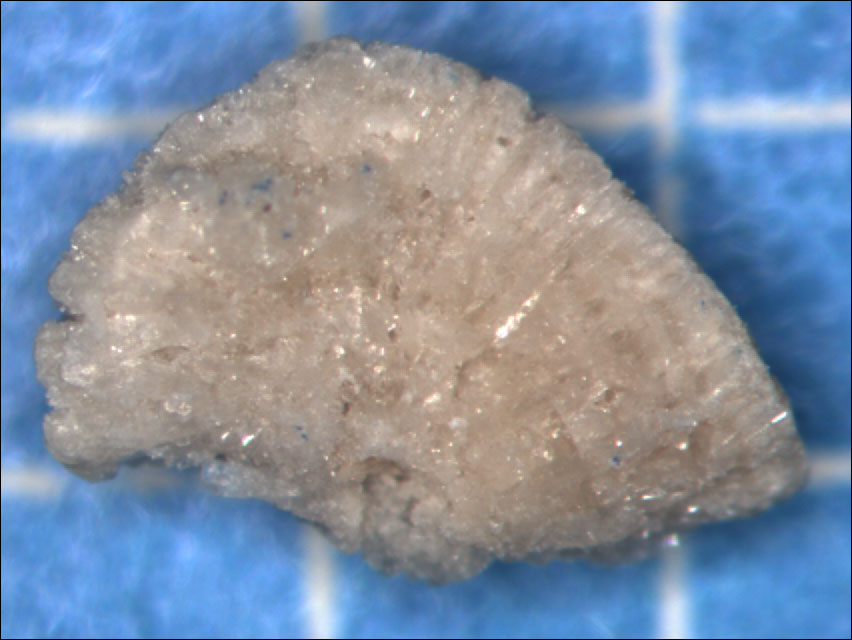
Brushite (also Epiglaubit ) is a rarely occurring mineral from the mineral class of " phosphates, arsenates and vanadates ." It crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system with the chemical composition Ca [ PO3 (OH)] · 2H2O, and is therefore a water-containing, basic calcium phosphate or the dihydrate of calcium hydrogenphosphate.
Brushite most developed prismatic crystals with acicular or tafeligem habit to about two inches size. Intact surfaces have a glass-like luster, cleavage surfaces shimmering mother of pearl, however, rather similar. Rarely occurs on brushite in foliated or earthy - powdery, matte mineral aggregates. In pure form, the mineral is colorless and transparent. Through multiple refraction due to lattice defects or polycrystalline training but it can also appear white and accept by foreign admixtures a light yellow color, the transparency decreases accordingly.
With a Mohs hardness of 2.5 brushite belongs to the soft minerals that can be scratched by a copper coin lighter than the nearest reference mineral calcite (3).
Special Features
Brushite is piezoelectric, builds so similar to the known quartz with varying elastic deformation of an electrical voltage. Add hydrochloric acid (HCl ), it is easily soluble.
Etymology and history
The mineral in guano on the claimed by Venezuela Aves Island was first discovered (in Spanish Isla de Aves, " Bird Island " ) and 1856 by Charles Upham Shepard initially called Epiglaubit, but described only incompletely. A scientifically precise description was followed in 1865 by Gideon Emmet Moore ( 1842-1895 ), who named the mineral after the American mineralogist George Jarvis Brush.
Classification
Already in the outdated, but partly still in use 8th edition of the mineral classification by Strunz was one of brushite to the mineral class of " phosphates, arsenates and vanadates " and then to the Department of " water -containing phosphates without foreign anions ", where he was named the " brushite group "with the system no. Formed VII/C.25 and the other members Churchite - (Dy ), Churchite - (Nd), Churchite - (Y) and Pharmakolith.
The 9th edition used since 2001 and valid by the International Mineralogical Association (IMA ) of the Strunz'schen Mineral classification assigns the brushite also in the department of " Phosphates without additional anions, with H2O" one. However, this is further divided according to the relative size of the cations involved, so that the mineral is found according to its composition in the subsection " Exclusively with large cations " where there along with Ardealit, Churchite - (Nd), Churchite - (Y) and Pharmakolith the " Churchitgruppe " with the system no. 8.CJ.50 forms.
The mainly common in English-speaking classification of minerals according to Dana assigns the brushite in the class of " phosphates, arsenates and vanadates " and then in the Department of " Water-containing acidic phosphates, etc. " field. Here he is with Pharmakolith in the unnamed group 39.01.01 within the subdivision " water containing acidic phosphates, etc., A [ HXO4 ] × x (H2O) " to find.
Education and Locations
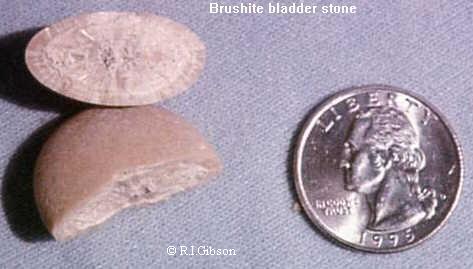
Brushite is formed predominantly in guano deposits, but can also be a component of urinary stones and occur as secondary education on human and animal bones. Accompanying minerals include Ardealit, gypsum, hydroxyapatite, Tanarakit and Variscite.
A rare mineral brushite formation could be detected only in a few localities, where so far (as of 2014) are about 80 localities known as. Apart from its type locality, the Aves Island, the mineral in Venezuela was found still in the " Cueva de San Sebastián " in the state of Aragua, and in the " Cueva Ricardo Zuloaga " and the " Cuevo del Indio " in the state of Miranda.
In Germany, brushite among others at Lüneburg limestone mountain in Lower Saxony, in the zinc smelter birch dish (also Friedrich- Wilhelm- hut) near Aachen and on the slag heaps of a copper smelter near Kall in North Rhine -Westphalia, at Schneeberg and Pawel Gear at Oberschlema in the Saxon Ore Mountains and in the pit " Jeremiah happiness" ( Fairy Grotto ) at Garnsdorf found in Thuringia.
In Austria you know the mineral so far mainly from Carinthia, where he and rock samples from the Kaponig tunnel construction in Moelltal in Ankogelgroup and in some findspots at Lanisch in, among others, the " small misery glacier " (small misery Valley ) for Hafner group belonging Pöllatal. In addition, is also ever a find point at Türnitz the Mostviertel and the vineyard at Amstall in the district of Krems- Land in Lower Austria, the Windisch head - bear cave in Tennek (municipality throwing) in Salzburg and the Pit " Roßblei " (or Ross lead) on the Eschach Alp Sopra known near the community of Rohrmoos -Untertal in Styria.
In Switzerland brushite previously came to light only in the Burgdorfer church in the Bernese Emmental and in the Payerneer Church in the Vaud Canton, when he was found in excavations 1968-1969 or in the 1950s to human bones.
Other localities lie among others in Algeria, Antarctica, Australia, the Bahamas, the British West Indies, Denmark, France, Italy, Japan, Kenya, Kiribati, Malaysia, Mexico, Morocco, Namibia, Puerto Rico, Reunion, Romania, Russia, Slovakia, Spain, South Africa, Hungary, the United Kingdom ( UK) and the United States of America (USA).
Organic Education
Brushite can be caused by precipitation from the urine in the urinary tract and thus lead to urinary stones. However, since brushite is highly soluble, this mineral rarely occurs in urinary stones. Conditions are a high content of calcium in the urine and a pH of between 6.5 and 6.8. Higher pH values lead to the formation of ( Ca2 (PO4) 2) in more acidic conditions, the solubility increases rapidly. Medically include brushite stones to the hard stones, which are relatively difficult to treat and can hardly be destroyed by an extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. In addition, they tend to recur quickly.
Brushite may also be involved in the formation of tartar.
Crystal structure
Brushite crystallizes in the monoclinic space group A2 / a ( Raumgruppen-Nr. 15) with the lattice parameters a = 6.24 Å; b = 15.18 Å; c = 6.36 Å and 125.4 ° and β = 4 formula units per unit cell.