Manual transmission
A vehicle transmission, the transmission in the drive train of a vehicle, which translates the engine speed to the input speed. The gearbox is designed as adjusting or when changing gear ( see below); it is necessary in motor vehicles, to cause the spread of the speed range with the spreading of the engine speed range to cover.
The vehicle transmission is a Unter-/Sonderform the general transmission, as the term is defined in mechanical engineering: In general, devices for any kinematically coupled conversion or implementation of movements " transmission " called.
- 3.1 Semi-automatic gearboxes and transmissions with torque converter clutch
- 3.2 Automated Manual 3.2.1 Classic automated manual transmission ( AMT) 3.2.1.1 Pros and Cons
- 3.2.1.2 dissemination
- 3.2.2.1 Pros and Cons
- 3.2.2.2 dissemination
- 3.3.1 Pros and Cons
- 3.3.2 Function and Control
- 3.3.3 Operator manner
- 3.3.4 safety
- 3.4.1 benefits
- 3.4.2 disadvantages
- 3.4.3 history
- 4.1 Primary gear
- 4.2 Transfer Case
- 4.3 range gear
- 4.4 Hydraulic Transmission
- 4.5 Automated Range splinter groups gearbox
Need a manual transmission
A gearbox is needed, if the spreading factor is different before and after the transmission. ( The spread factor is the ratio of the greatest value to the smallest value, where: speeds)
A car had a minimum speed Vmin = 5 km / h ( closed clutch ) and a maximum speed Vmax = 250 km / h This results in a spreading factor == 50 for the propeller shaft ( the " output" of the vehicle transmission ). The internal combustion engine has an idle speed of 600 rpm and a maximum speed of 6000 rpm, so a spreading factor of 10 without gearbox could be the car when 600 rpm engine speed to 5 km / h led, so reach a maximum 50 km / h.
Manual operation
Manual transmission
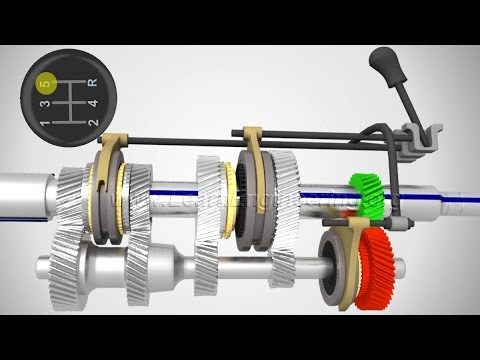
With a manual transmission - also called change gears - the speed ratios are formed by the gear pairs. The most common version of a manual transmission is that of the spur gear. Is switched by the switching mechanism in the transmission. This gear mechanism in turn is connected via a rod or cable to a shift lever.
The torque is transmitted to the transmission input shaft of the clutch through a spline. On the transmission input shaft, the gears of the individual gear stages are mounted. Comb with either the gearbox output shaft or counter shaft, the output shaft coaxial ( alignment ) is attached to the input shaft and there is a direct transition, ie, the waves are coupled and the translation is exactly 1:1. The gears of both waves form pairs and engage with each other. The gears are fixedly mounted depending on the design on the waves or rotating freely ( but axially fixed). In order to produce a frictional connection between the shaft and the freely rotating gears, they are fixed with a dog clutch on the shaft. A dog clutch is fixed radially to the shaft and can be displaced axially. Are located on the flanks of the tooth profiles, their counterparts find themselves in the gear flank. For a switching operation of the dog clutch of the shift fork is pressed against a toothed wheel. Snap the tooth profiles of gear is engaged. To make the switching process gentler, are used in automotive transmissions to the sides of the jaw clutches synchronizer rings. Synchronizer same before the engagement of the rotational speed of the gear wheel to the rotational speed of the shaft. In general, the gear wheels are helical gears; order to keep the noise low and transmit greater torques, more teeth are engaged at all times here. However, caused by helical gears axial forces that need to be taken from storage, except for the herringbone gearing. There, the same opposing helical gears ( in a gear ) from the axial forces. For reversing, a reversal of direction is required. This is realized by a further gear wheel. To change gears, the power flow must be interrupted. This is effected by a coupling. Here, the driver operates the clutch lever, the clutch disengages and can with the shift lever and the associated switch mechanism in the transmission a gear change ( shift ). The manual gearbox is still the most commonly encountered of transmission in motor vehicles.
Operation
An example is the transmission of a vehicle with a front engine and rear wheel drive.
In the closed gear casing extend two shafts: the main shaft, which leads seen visually from the input to the motor flange to the drive shaft and the output is interrupted after the first gear stage and the counter shaft which is parallel to the main shaft.
From the front part of the main shaft, starting the countershaft is driven by the first gear wheel pair. By switching the respective following gear stage, the torque is guided by the intermediate shaft to the rear part of the main shaft and from there further to the output. The individual gear pairs are synchronized with the transmission engaged at all times. A gear is fixedly connected to the shaft, the other can with a shift sleeve, a positive connection with the shaft to be turned. In general, the shift sleeves sit on the main shaft, but they can also be located on the countershaft. By coupling the two parts of the main shaft of the output is directly driven ( direct gear ), the countershaft runs in this case, but without transmitting torque.
The gears are now connected as follows:
H circuit
If the transmission is in neutral, none of the gear wheels is connected to the drive shaft. The power circuit is interrupted. All gears of the drive shaft and countershaft are constantly engaged, but no power is transmitted.
To engage a gear, the frictional connection between the engine and transmission must be interrupted. The purpose of the clutch. The drive part of the main shaft comes to a stop after a short time.
A rotary - sliding mechanism makes sure that the shifter pawl is actuated by the movement of the gear lever, which pushes the body responsible for the selected gear shift shaft with the shift sleeve between gear wheel and countershaft. A rotary movement of the switching rod is shown in simplified form by a movement of the gear lever by the idle -Gasse triggered in the transmission, each causes the shift finger to access a switching shaft, which can be moved by the switching claw in two directions. A sliding sleeve which is displaced by the pawl on the shaft, that is responsible for two passages. One could say that a front-back movement of the shift causes a shift of the claw, and a right-left movement rotates the shift rod and selects a different operating shaft. Hence the H-shaped arrangement in the shift gate. A four-speed transmission has three shift shafts - two for the forward and one for reverse. The reverse gear is engaged via a third transmission shaft.
(Also known as stick shift ) by pushing the shift lever in the alley the selected gear so a shift sleeve on the drive shaft between the gear wheel and driving wheel is pushed. The gear wheel is rigidly connected to the shaft and the traction produced within the gearbox.
H circuits leave a free gear selector to ( at least theoretically): It can be switched from each course in each other ( during operation should be but this is not done the reverse gear ).
Sequential transmissions
Sequential transmissions can not be selectively unlock only sequentially. It can only be changed in each of the next higher or lower gear, but it is not possible to skip one or more gears.
Such a transmission is found for example in the Smart Fortwo and motorcycles.
A common sequential gearbox is the Kegelzuggetriebe. In this gear type is omitted, the shift dogs, the countershaft is hollow. Within the counter shaft, a cone is attached to a rod. This pushes through holes in the counter shaft to the gear wheels balls to the outside, which provide a positive connection between the shaft and gear wheel. A slightly modified design is the draw key transmission in which a grooved shaft in a draw key when changing gear is moved along and locked the respective gear with positive locking. Examples: Gear of the moped and mopeds Zündapp, DKW and Samson.
Synchronization
Is initiated at a non-synchronized transmission of gear changes in speed difference, the difference must first be equalized. If this condition is not satisfied, a rattle is one that accompanies the switching operation at the unsynchronized gears. Cause is designed as a multi-tooth sleeve shift sleeve which is pushed into the running at a different speed clutch body of the gear wheel. So it was earlier on the skill of the driver, as noisily, the switching operation has been performed.
To prevent the noise, there are two techniques: External and internal synchronization. With internal synchronization, which takes place at synchronized transmissions application, worried that one of the shift sleeve upstream synchronizer ring. This usually consists of a base body made of brass, formed steel plate or a steel sintered material. He is provided with an additional special Sinterreibschicht or applied by plasma spraying molybdenum coating. Carbon deposits also be used. This friction layers act as a cone clutch and create friction between gear wheel and countershaft. This is similar to the speed until the shift sleeve can finally slip into it. A distinction is made between simple synchronization and forced synchronization (also blocking synchronization), in which the shift collar engages only when properly synchronized.
In unsynchronized transmissions external synchronization is required. In older designs, it was in the driver's responsibility to equalize the speeds of both ends of the power cord. The adaptation was pure emotion and experience thing. Before the upshift is idle engaged briefly ( intermediate coupling ) to decelerate the drive shaft ( or the countershaft ). This is necessary because the gears of the next gear have a slower peripheral speed. When downshifting is also engaged at idle, but it may soulful gas ( intermediate gas). The gear wheels on the drive shaft are adapted to the peripheral speed of the gear wheels of the smaller gear. Due to improper operation of the transition can be difficult or impossible are inserted. This inevitably leads to damage to gears ( thrust wheel gear ) or shift dogs (thrust mesh gearbox ).
Even if the intermediate coupling or intermediate throttle in a gear with internal synchronization is not necessary, it can at proficient application lead to more rapid and gentle shift. For small gears in the car sector, the effect is not very pronounced in truck with correspondingly heavy transmissions, however, often quite noticeable.
A transmission with lock synchronization can be switched in an emergency without a clutch. When the clutch is no longer functional, starts with pickled first gear the engine. The driver wants to turn, he gives slight train to the shift lever, which then jumps shortly after the gas removal in "Neutral". Now waiting until the engine by ear has approximately the speed of the next higher gear selected, and then slight pressure is applied to the shift lever. Is the speed, " slips " in the gang. Downshifting is similar to the unsynchronized transmissions, achieved by accelerating and waiting. At a red light may only be moved very slowly to avoid a stop, thus ensuring a restart. This procedure is applicable only for experienced drivers in an emergency, since the synchronizer rings on a permanent basis subject to heavy wear.
Without the clutch you should go only in an absolute emergency, because the risk of failing to bring the vehicle to a stop in time ( and therefore to cause an accident ), without using the clutch is high.
Newer, mostly automated gearbox or sequential gearbox in motor racing are synchronized by an electronic motor speed adapts so that a trouble shifting the engine is possible.
An irrelevant in racing, but very desirable in road vehicles benefit is the lower noise. Schieberadgetriebe almost always have straight-cut gears, in which the sudden engagement of the teeth caused a yelp. With claws connected or against synchromesh allow the use of gears with helical teeth and softer tooth engagement.
Schieberadgetriebe
In Schieberadgetrieben the gear wheels are almost always straight teeth and the hub and gear shafts splined, so do not rotate on the countershaft. They are moved on the shaft when shifting and so are not engaged at all times. Such transmissions without synchromesh can upshift with declutches down and with intermediate coupling and spur gears in operation generates a characteristic loud howling sound (as in modern cars nor the reverse), but they have a higher efficiency. Schieberadgetriebe were widely used before the introduction of synchronization in the 1930s, and then were far only the upper gears synchronized by the Second upwards. The last German car with a Schieberadgetriebe was the Lloyd LP 300 the VW Beetle I. and II transition were initially designed as sliding wheels, III. and IV helical teeth ( " noise " ) with jaw-type shift (as round pins running).
Gear for racing applications, also called short racing gearbox are still built as Schieberadgetriebe today. This allows for the same dimensions a higher load capacity ( larger maximum transmissible torque ) because waves can be more powerful unit (interesting for rally cars and vehicles Cup class ), or reduced weight (with touring and racing cars). The current trend in racing goes to uninterrupted high shifting transmissions ( due to the high air resistance and low weight atone racing car in a ' normal ' gear change 2-3 km / h ). For this, two gears can be loaded at a short time. To prevent transmission loss, there are several possibilities. One is the use of one or more free wheels, so that when overlapping an upshift the faster rotating wheel to the higher path overtakes the slower rotating gear of the lower gear. The freewheel prevents this is that the transmission is distorted. Another variant consists in that for a short time (a few milliseconds) are inserted two gears simultaneously. To make this possible without tension, a backlash between the gear wheels and its shaft is required. If the previously engaged gear is not pulled in time, there is a transmission failure. In switching operations, there is very strong switching transients, therefore, such types of cars are unsuitable.
Automated operation
Semi-automatic gearboxes and transmissions with torque converter clutch
A special form of transmission are semi-automatic transmission, which you do not have domes, but even on. When you touch the shift lever is disengaged automatically when the next gear is engaged, reengaged. In principle, they are mechanical transmission with an automatically -operated single disc or magnetic powder clutch.
For gearboxes with a torque converter clutch (WSK) a conventional manual transmission is combined with a torque converter, which is located between the engine and clutch and a conventional automatic transmission from her well-known comfortable wear-free starting and maneuvering possible. To change gears, the driver must operate the conventional clutch as in a normal manual transmission, to interrupt the flow of power and also change gear manually. Today, this design is mainly used in heavy-duty truck.
In some vehicles, both concepts (semi-automatic transmission WSK) were combined.
Examples of vehicles with semi- automatic transmissions are built in Ford 17M, the VW Beetle and Karmann Ghia, the DKW F 11/12 and AU 1000 and Opel Rekord ( " Olymat " ) Saxomat, and also the Renault 4CV and Dauphine available on request Ferlec magnetic powder clutch, the WSK with additional automated clutch the Mercedes 219/220 S/220 SE ( " Hydrak " ), Porsche 911 ( " Sportomatic " ), NSU ro 80 (standard), Citroën DS and Renault Fregate ("Trans fluids " ) or the more recently available Citroën CX C -Matic. For the Trabant there under the name Hycomat a semi-automatic gearbox.
Since the early 1990s, there is also loss-free working semi-automatic gearbox with automatic clutch system, which turned by hand and the conventional disc clutch is electronically -hydraulically operated, for example, the Renault Twingo 'Easy', the Mercedes -Benz A-Class W168 with automatic clutch system ( AKS ) and Saab.
Automated Manual
Automated manual transmissions, known in English as well as Automated Manual Transmission [ AMT], due to specially tuned driving programs the transmission control enable the combination of increased ride comfort through a user-friendly transmission control with the economy through reduced fuel consumption and reduced emissions. For this reason, for example, drew in a 3 -liter Lupo Volkswagen of an automated manual transmission used.
The main difference between the treated hereafter ASG and DKG is that only one clutch is available at the ASG. A disadvantage is the interruption of tractive power - the power flow must be interrupted to switch briefly. It is advantageous that the clutch is normally closed and only open energy needs, which is why the ASG is usually installed in a particularly economical and light vehicles.
When DKG two couplings are present: It is advantageous that the opening of a clutch, the other at the same time close and so the tension is not interrupted. The disadvantage is that both clutches are open in the resting state and the clutch must be locked in the active power branch with energy.
Classic automated manual transmission ( AMT)
An automated manual transmission, also called automatic gearbox is a conventional manual transmission, which has been extended by automated switching components. The fundamental difference with a manual transmission is that the gear change is not performed by the driver, but by means of hydraulically actuated cylinders and electric control motors, the so-called actuator. During the gear shift of the driven clutch separates the tensile force is then passed through the stored in the transmission control unit gearbox logic, the calculated gear change from the driver to the shift actuator of the transmission and the transmission shifts depending on the driver's request in the next higher or lower gear.
The switching operations for automated manual transmission will automatically be from the transmission performed by the stored in the control unit circuit program or else there is for the driver the ability to switch through the selector lever on the center console or the paddles on the steering wheel by tapping the paddles forward to the next gear, switch or by tapping back into the next lower gear. By switching program ensures that switching errors. In general, it is only possible to skip gears. Such switching operations can only be executed by the electronics when the motor in this case is within a permissible speed range.
In trucks, especially for long haul, come since the mid- 1980s such automated transmission is used, in which the driver selects the appropriate gear and the electronic transmission via electro-pneumatic shift cylinders control the transmission shifts. In the classical EPS of Mercedes -Benz, the driver selects, for example, the "6 Transition / low " and actuates the clutch pedal. Characterized the electronic control unit is activated and checks to see if the shift operation may also be performed due to the respective engine speeds. If this is the case, the electronic control unit switches on the pneumatic switching cylinder in the respective passage. Denies them the shift because the engine threatens to turn, this is indicated to the driver by a warning sound. In general, the transmission switches to idle.
Newer systems in the truck or bus switch also be fully automated; a clutch pedal is missing or can be folded out for emergencies. By default, modern trucks are equipped with an eight-speed transmission. Basis of the truck transmission is usually a four-speed manual transmission, which can be expanded with a upstream group and a range group, so 16 grades are available.
Pros and Cons
Most of the benefits divides the ASG with the manual transmission:
- Comparatively simple mechanical structure,
- Good efficiency because no circulating lubrication or churning of the oil occur and
- Many identical parts, so that the large number of pieces leads with manual transmissions from low- cost.
In addition, it offers other advantages:
- Compact design, because the actuator requires only low power and are built according inexpensive and space-saving can
- All the actuators of the ASG is active only during the switching process and therefore consumed only in this situation, energy
- The usual advantages of automatic transmissions as security against stalling, wiring and engine overspeed and strategies for optimal consumption to special sportiness or for spares the engine during the cold start phase
The main disadvantages are:
- Tensile force loss during the switching operation, and
- Long switching time,
Particularly under load lead to tangible scarf Trucken and are expected only in exotic sports cars of the customers.
Against the disadvantages use newer ASG a second countershaft on which (as in DKG ), the switching operation for each of the adjacent transition can be prepared so that the interruption of traction on the time for the brief release the clutch (50 ms at ISR Graziano in the Lamborghini Aventador ) is reduced.
The first used on a large scale vehicles automatic transmission were equipped with hydraulic actuators 1997, the BMW M3, in which the existing classical manual transmission was upgraded by means of hydraulic toward automatic transmissions, and 1998 Smart Fortwo, the first vehicle was an electric motor- operated automatic transmission. The special feature of the smart was that his gearbox was offered solely automated and there is the "manual" option, only operated as a program lock changing the software in the transmission control. A first " manually " to be switched Smart can easily be automated by software change. Both transmissions were developed by Getrag.
Dissemination
Because of the low efficiency is especially in small cars, the ASG a popular trim level, so among other things, the Audi A2 1.2 TDI, Opel Corsa, VW Lupo 3L or smart. The VW Group three-liter car but the gearbox with relatively high proportions of damage and very expensive replacement gear made negative attention to themselves; often be offered with a defective transmission control (as of 2011 ) on the second hand vehicles.
Automated manual transmissions are offered by various car manufacturers with different brand names:
- Alfa Romeo: Selespeed
- Audi R tronic
- BMW: SMG
- Citroën: SensoDrive, EGS, EGS6 ( Electronic Gear Shift = electronic gear shift ), ETG6 (Efficient Tronic Gearshift )
- Fiat: Dualogic
- Ford: Durashift EST (Electronic Shift Technology)
- Honda: i- Shift
- Lamborghini e -gear and ISR (Independent Shifting Rods )
- Lancia: DFN ( Dolce Far Niente, Italian for Sweet idleness )
- Mercedes- Benz: Sprintshift
- Mitsubishi: Allshift
- Opel: EasyTronic
- Peugeot: 2 -Tronic, EGS6
- Renault: Quickshift
- Smart: Softtip Soft touch on newer models also Softip Softouch
- Toyota: MMT ( MultiMode transmission )
- Volkswagen: Shiftmatic (SMC )
Dual-clutch transmission (DCT, DSG, PDK)
A relatively new variant of the automatic transmission is the double clutch transmission ( known as " direct shift " or " DSG ", English: Direct Shift Gearbox ): It consists of two automated partial transmissions, each with an associated coupling. One transmission unit transmits the even gears, the other the even gears and the reverse gear. Before shifting to the switching transition is first inserted in the load- free branch. Then, the coupling of the non-load passage is closed and the other of the gear simultaneously. This can be switched without interruption of traction - the time required for the gear change depends only on the switching speed of the couplings.
Pros and Cons
The main advantages of the DCT are:
- Shifting without interruption of traction, but only in neighboring transitions ( even-odd )
- Very fast switching, suitable also with manual operation for use in racing
- High efficiency in comparison with transducer automatic
- Favorable space requirements for vehicles with front - transverse engines
- Many identical parts with manual transmissions, so that the large number of items leads to low cost
- The usual advantages of automatic transmissions, such as security against stalling, wiring and engine overspeed and strategies for optimal consumption to special sportiness or for spares the engine during the cold start phase
The disadvantage compared to the ASG is the permanent energy needs to be kept closed during power branch the clutch.
Because of their properties are DSGS compete with conventional machines with torque converter and planetary gears.
Dissemination
Originally developed by Porsche in the 1980s for racing, Volkswagen and Audi were the pioneer in the use of this technology in large-scale and could hereby develop a technological edge in the market. Since 2002, a dual clutch transmission in the Golf and Passat class is used in series (6-speed, a supplier to the wet clutch is Borg Warner ). The VW internal designation is DQ250 ( for dual clutch cross recessed 250 Nm, which it can transmit 320 Nm).
In the following years, a 7 -speed DSG came out with the internal designation DQ200 (Polo and Golf small class) from VW. For this purpose, LuK supplies a dry double clutch.
In 2009, the first developed specifically for Audi DSG came to be called DL501 with the Audi Q5 on the market. In this transmission comes back a wet-running double clutch Borg Warner used. DL501 stands for dual clutch longitudinal recessed 500 Nm and comes in models A4, A5, A6 gradually used.
Last followed in the fall of 2009, the DQ500 ( 7-speed DCT) for the VW Bus T5; it is also offered for the Tiguan since June 2010. The wet clutch is designed and manufactured by the VW Kassel plant, which is the first time a self-developed by VW dual clutch used.
All variants ( DQ200, DQ250, DQ500 and DL501 ) are manufactured at the Volkswagen plant in Kassel.
Since July 2008, Porsche offers the 7-speed PDK ZF for the new 911. For the Boxster and the Cayman, it is also available to order. Since September 2009, there is also the PDK for the Panamera and, since October 2009 for the turbo. For the BMW M3 is a dual-clutch transmission with seven forward gears Getrag has been available since March 2008. Ford, Mitsubishi, Ferrari, Mercedes -Benz and Volvo have since 2008 also models with dual clutch transmissions from Getrag on offer. For the first time a DKG is installed in a production bike the brand Honda (VFR 1200) since the summer of 2010.
Converter automatic transmission
A converter automatic transmission is different in structure from a manual transmission primarily by the following points:
- The ratios ( transitions ) can be achieved with a different number and combination of planetary gears (see also Lepelletier (6 levels), Wilson set ( 5 levels), Ravigneaux (4 levels), Simpson set ( 3 levels) )
- Synchronization elements ( unlike the ASG and DKG ) multi-disc clutches, multi-disc brakes, clutches or brake bands (deprecated).
- Serves as starting a hydraulic clutch ( Föttinger coupling, pure speed transducer, outdated ) or a torque converter ( Trilok converter )
Pros and Cons
Are considered essential advantages of the transducer automata:
- When using a Trilok converter the starting torque on the motor side is available again increased significantly.
- The converter dampens vibrations in the drive train, unless it is just not bridged.
- Particularly small jolt ( smooth shifting ).
- High torque density and compact design due to planetary
The best-known disadvantages are:
- Poor efficiency and consumption disadvantage by permanent circulation lubrication and drag losses open circuit elements
- When the lockup clutch is closed, the torque peaks of the engine must be intercepted. While manual gearbox to use dual-mass flywheels, the lockup clutch is used in many machines do not completely closed, so that they permanently runs with 20-60 1/min in the slip. This slippage also reduces the efficiency.
- Towing with a rolling drive axle is not possible on all models or only over short distances, because damage may occur in the transmission due to lack lubrication. Towing over long distances requires a second oil pump on Achsabtrieb (older Mercedes vehicles ).
- High costs, for example by the production of close tolerances in the hydraulic control box
- In many types a regular transmission oil change is still required.
In exceptional cases, dispense with automatic transmissions on planetary gear sets, as for example in the Honda Automatic transmissions and the automatic transmission, the Mercedes -Benz A-Class ( W168 ). The construction of such transmission similar to a manual transmission. The essential distinguishing feature is that instead of syncs and shift sleeves for each switching stage of the automatic own multi-disc clutch is available.
The non-positive connection of the individual planetary gear sets with the input and output shaft provide multi-plate clutches ago. The movement is defined by a drive and switch program in the control unit. The control of the gear was hydraulically until the late 1980s. At the present time (2008 ) it is controlled electronically and the actuation of the clutches of driven electrically by means of hydraulic valves.
Function and Control
In the torque converter, a part of the engine power of the generated slip of the oil is discharged in the form of frictional heat. In order to reduce the associated efficiency loss, current transformer are often equipped with an automatic transmission torque converter lockup clutch, which allows the start-up or after the change of the speed steps a direct mechanical force fit.
Is further required for the generation of the hydraulic pressure by the oil pressure pump energy. The unused level in the inserted empty follower plate clutches additional drag losses are generated because the couplings are open. By these drag losses of the fuel consumption in comparison with an otherwise identical and equipped with manual transmission vehicle is higher. Modern automatic transmissions offer a mechanical torque converter lockup already from first gear to reduce this increase in fuel consumption. More consumption reduction allows the decoupling state that the transmission shifts with the vehicle stationary and operated service brake to idle, thus preventing the drag losses across the transducer. The exchange cons of automatic show is usually the standard consumption - as opposed to the consumption occurring in normal traffic - barely, as the shift points are adjusted to the standard cycles.
A step change is carried out by turning off a switch element and simultaneous connection of the switching element for the next higher or lower level. Thus, the second switching element takes over, piece by piece, the torque from the first until the end of the step change all of the torque is transferred from the second switching element. The time period for this grinding process moves in the two -to three- digit millisecond range. Since the introduction of electronic transmission controls the end of the 1980s, in order to protect the transmission from overload and / or to achieve a better shift quality, transmits a " Torque -down" request to the engine control unit. Since the late 1990s, this is done via the CAN bus. Which causes the motor control to reduce the driving torque for the duration of the shift. Another means of increasing the shift quality is to open the lock-up clutch at predetermined switching situations. The gear change between up to eight gear ratios very soft. That the power flow by design does not completely shut, also leads to the well-known " creep" of the coupled vehicles with automatic transmission ( as long as it is not in idle). This circumstance can be very beneficial when maneuvering.
To the electronic control system ( for example, the EGS), further effects can be achieved: At low drive levels, it is now common practice to limit the torque of the motor. This allows the couplings are designed to be smaller in the automatic transmission and the rest of the drive train must be designed for a lower torque, which makes this easier and cheaper. At the same time when the brake and the accelerator pedal is depressed, the controller prevents that the engine is clamped to the drive train, overloaded and overheated transducer. When kick-down, wheel slip is controlled along with the ASR. In the spinning of a wheel which is regulated by a brake intervention. Turn all driven wheels, the engine power is limited.
The kick-down function ( About gas) could already be found in early - converter automatic transmissions with a purely hydraulic control. A signal is beyond the mere addition throttle thereby sent to the controller of the automatic transmission by operating the kickdown switch to the stop of the accelerator pedal. The automatic shifts into gear with the best possible acceleration and causes the motor to high speed. It is expedient to use the kickdown especially when overtaking.
When switching back to the principle of multiple downshift is used in more complex converter automatic transmissions: The switching process takes place, where appropriate, by way of snap action. Thus, gear ratio, but usually only a skipped. A selectable in modern vehicles switching program is usually overshadowed by the kickdown signal.
Operating manner
Usual is a lever on the vehicle's center tunnel with the setting
In automatic transmissions usually this order is respected as exist, for example in the U.S. legal requirements for it.
Some vehicles may offer more speed steps, often is a manual mode possible:
Security
Cars with automatic gearbox must transducer after a failure - depending on the manufacturer - only over short distances or not be towed if the driven axle rolls. Without running the engine, the oil pump is not driven, so that a sufficient lubrication is ensured in most transmissions. An exception to this converter automatic transmission with an additional secondary oil pump on the gearbox output, for example older converter automatic transmission from Mercedes -Benz.
In the 1980s there were security problems with alleged " self-perpetuating " or vehicles that accidentally took up a travel movement. In the U.S., appeared TV reports in which it was alleged that vehicles (mainly Audi models were shown) would set despite stepping on the brake unexpectedly moving. A final determination has not been reached, as a result, however, some security features have become naturalized:
- The key can be removed only in the "P" position, the locking of the steering wheel lock when the vehicle is rolling is thus prevented.
- The engine can only be started in the "P " and / or "N". A Roll on with the start of the engine is not possible.
- To exit the "P" position, the brake must be pressed. For some manufacturers, this also applies to the "N" position (only with vehicle stationary ). The driver is then forced to press the right pedal when starting. Thus, a mistake of the accelerator pedal is to be avoided with the brake.
With the proliferation of these arrangements in new vehicles, the problem of self-runner has disappeared. Meanwhile, additional backups have taken hold. Thus, in some automatics increase the engine 's power hardly, if at the same time the brake pedal is depressed. Any distortion of the drive train and overheating of the converter are thereby excluded.
Continuously variable transmissions
- Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) is a continuously variable transmission with the (limited ) transmission range, corresponding to that of manual transmissions. After DAF transmission ( Vario Matic ) there were attempts by Fiat, Subaru, Ford, Mini and Mercedes -Benz ( under the name Autotronic in the A-Class and B-Class ) Today CVT under the name Multitronic Audi available in A4 and larger models, under the name of Subaru and linear Tronic CVT simply as Honda Jazz and the Civic hybrid. In addition, most scooters and more recently, some motorcycles CVT transmission.
- Infinitely Variable Transmission ( IVT) has an ' infinite ' field of translation, that is, at 1: ∞ is stationary the transmission output shaft, although the input shaft is connected with the engine running, so that in this design no clutch is required.
Although a planetary gear or as a summing transfer gearbox is not infinitely variable, but may act pseudo- continuously, an input shaft, if the second input shaft ( of the summing ) compensates accordingly ( " regulates the total ratio "). The second input can be executed, for example, hydrostatic ( tractors ), electric ( Toyota Prius ) or mechanically (CVT ).
Benefits
This gear design offers the following advantages:
- Elimination of switching stages, thereby because torque and speed change is better comfort continuously and not in jumps
- No switching pauses, since no shift is performed
- Consumption: the engine is running whenever possible in the area of the best current fuel consumption, and in drag mode can be selected by the translation adjustment the smallest drag torque
- Dynamics: when maximum acceleration is expected, the motor during acceleration can always run at maximum power, the speed can be adjusted solely by the ratio of the CVT
- Noise: the engine is run in each quietest operating range
- Exhaust emissions: the engine is operated within the operating range of the least polluting emissions
Disadvantages
- In many types strongly limited torque capacity
- Increased technical effort, some special types of oil required
- Limited customer acceptance
The torque capacity can be improved, for example with a power splitting. Here, the continuously variable transmission is combined with a summing planetary gearbox or branching. This, however, the spread of the translation is either reduced, or it worsens the overall efficiency of the gearbox combination.
With fuel-efficient characteristics of the disadvantage of poorer transmission efficiency can be partially offset. Through the consumption optimizations on the engines and wider speed belts for the best fuel economy, the dual-clutch gearbox are currently the most important competitors of fuel-efficient CVT.
In practice, it can not be realized unilaterally optimized characteristics for lack of customer acceptance, so that the theoretical benefits are subject to certain restrictions.
Experience has shown that many drivers are not satisfied when the vehicle during acceleration from zero to 100 km / h always with the same engine speed drives ( " rubber band effect "). To avoid this, provide numerous CVTs to a switching program in which they work with fixed gear ratios and thus mimic a normal automatic stage.
History
CVTs have been used as standard first in the Dutch DAF automobiles under the name VARIOmatic from 1961. In essence, the power in continuously variable transmission is transmitted via V-belt between belt pulleys with variable spacing (see CVT).
This principle according to Van Doorne has now been further developed with rigid chains of metal elements for higher torques. These transmissions were in the Ford Fiesta, Fiat Uno and others. Audi came around 2000 with the new Multitronic gearbox for high performance car on the market. In it affects a pulling rocker joint chain.
Also equipped with a hybrid drive Prius has a continuously variable automatic transmission, which does, however, a power split planetary gear that connects the internal combustion engine with two motor generators. The gear ratio is made purely electronically by the variable control of the motor generators. A separate reverse gear is unnecessary. Furthermore, account for a torque converter. However, " creeps " and the Prius, that is, it is composed of the state without accelerating the move. The continuously variable transmission of the Prius is part of a designated as Hybrid Synergy Drive unit consisting of combustion motor, planetary gear and two motor generators.
The equipped with a hybrid drive Honda Civic Hybrid has a continuously variable CVT transmission with a torque converter.
Similar to the transmission function of the Prius power-split hydrostatic transmission, which are particularly common in tractors. The power is branched via a mechanical part and a variable hydrostatic part. Through infinite adjustment of the translation in the hydrostatic part, the resulting overall ratio can be controlled. In order to improve the overall efficiency, such transmissions have some still additional grades.
Spread in Western Europe
In international comparison, the percentage number of equipped with automatic transmission only passenger cars in Western Europe lags far behind countries such as the USA and Japan. This is due to some disadvantages compared with the manual transmission, among other things, lower acceleration capability when no converter elevation is present, lower top speed, higher consumption, delayed response at the start of an overtaking maneuver, premium over the manual transmission (not common in all markets ), other traffic conditions and on the sometimes unsportsmanlike Image of the automatic transmission, which is rare in the classical form of the converter with planetary gears in motorsports.
Additional transmissions in commercial vehicles
Primary gear
In this transmission is an extension of a conventional gearbox. In this case, an additional step is placed on the countershaft of the input shaft. This has the effect that you can pass each course in two stages. So there is for each course a small and a large stage. The single gear is so divided, or, as they say, " split ". This brings this transmission, called " Splitter" and the overall construction of the name "split gearbox" one. The term " primary gear " indicates that this transmission is installed before the base transmission. More often, however, the ballast group is housed inside the hub. Split gear can be found in heavy-duty trucks They are usually operated via a switch on the gear lever. If only the splitter is operated or is switched from a high to the next higher low gear, it is called " shift up half a gear". If you switch from a low in the next lower high gear, it switches to " half a gear down ".
Transfer Case
A transfer case is a used in construction after the base - gear transmission. It can be used in vehicles in which several axes are driven ( four wheel drive ). The transmission, the drive power distributed to a plurality ( in a 4 × 4- car two) axes through a drive for each axis. Depending on the type, the individual axes can be switched on and off. In addition, reductions can be integrated in the transfer case - this is often to be found in SUV ( Low Range ). The function of the transfer case is not to be confused with drive axles that have a built-in drive-through, such as heavy trucks with 6 × 4 drive.
Range gear
This gear is used in construction between the base gearbox and propeller shaft two-stage planetary gear. This doubles the number of shiftable gears, or even how to english says the "Range" ( [ reindʒ ], dt area). Therefore, hot designs using such a range gear, also called " range-change ", see also overdrive.
One first shifts the gears of the basic transmission and then actuates the "Range- groups switcher ". This is done via a switch on the gear lever or via the so-called " rollover ". In the former, the switch is in the upper (large ) group will be put before the shift, and then out of the gear lever back into the lane of 1st gear. However, this is the 5th gear ( with a 4 -speed basic gearbox ) or 4th gear ( on a 3 -speed basic gearbox ). The " rollover " the driver has a split 8-speed setting in front of him, which is interrupted between the alleys of the 3rd and 4th gear and the 5th and 6th gear. This leads to the gear lever after passing through the 4th gear into neutral and fails with the heel of the hand lever to the right. Result, the range group is changed and the lever no longer springs in neutral right now, but to the left. It is located from the rider now faces the alley of the 5th or 6th gear. In fact, the lever before the 1st or 2nd gear of the basic transmission is, but it is now by the break of the 5th or 6th gear. This is also called a " double -H " circuit. Such transmissions are found in heavy-duty trucks
Often pros and range gear are combined, allowing up to 16 speed steps are available in heavy-duty trucks available.
Hydraulic gear
Motors with a high torque output, which require a gear due to the above -mentioned narrow sense usable rpm band, can be found for example in diesel locomotives. Since extremely high requirements would result in a friction clutch with conventional gear when moving off, flow gear or are often called " hydraulic transmission " used in railway operation. When the gears used, a torque converter is used to start-up, the individual gears are connected without interrupting the tractive force by a fluid coupling is emptied while another is being filled with the same oil. Additional bridging couplings are still partly used in order to keep the energy losses attributed to slip. An example of diesel- hydraulic powered locomotive is the German DB Class 218
However, the alternative is the more commonly used electric power transmission, in which a generator is driven, the power supplies for electric traction motors.
Automated Range splitter group transmission
Modern trucks are equipped with automatic transmissions according to some of the above definition. These electronic shift aids were developed for commercial vehicles at the beginning of the 1980s with the desire to save fuel, protect the drive components as well as a driver's relief. Although these switching systems came in truck drivers in the early days with strong opposition, made in 1984 as the first manufacturer Scania an electronic switching means under the name of CAG ( Abbreviation of Computer Aided Gearshift ) on the market. The conventional shift lever is replaced by a short " joystick " on the engine tunnel. An electronic system, which affected various driving parameters such as speed and engine speed, gave the driver a shift recommendation display via the instrument panel. Accepted the driver to the proposed aisle, he needed only to operate the clutch. For a different gear selection, he turned on the desired gear by using the joystick. In case of failure of the system, the box with the selector switch was folded to the side and insert a conventional shift stick, which was carried in the vehicle.
About a year later Mercedes -Benz attracted as a manufacturer 's own commercial vehicle transmission and ZF Friedrichshafen suppliers by producing his own shifting teeth. Mercedes presented at the IAA 1985, the electro-pneumatic circuit (EPS), which was offered as standard in what was then the most powerful model in 1644. For smaller models as well as for the O 303 touring coach she was available for a surcharge. In contrast to the CAG of Scania and some models of ZF, the EPS was no gearshift recommendation, the gear selection therefore had to be always by tapping the lever forward or back (for high or downshift ). With introduction of the new Actros series followed in 1996 by the " Telligent " circuit ( portmanteau of " telematics " and " Intelligent " ), first as a semi -, later as a fully automatic circuit.
At the same time offered ZF as a manufacturer of truck transmissions, among other semi-automatic shift aids under the name AVS (abbreviation for Automatic preselector ) that could be operated via buttons, shift knob or a rocker switch on the steering wheel. In use, however, all systems are substantially identical initial: the driver is connected via a switch a switching pulse, which is converted by the electronic and pneumatic control cylinders. Today it is gone over to the driver remove virtually any work done. Only neutral and reverse gear be operated at all switching aids via special keys or key combinations. In some fully automated manual no clutch pedal is provided in the Actros is folded away, for example in the footwell and can be used optionally. As the electronics completely controls all shift and clutch operations, also unsynchronized dog gear can be used, which are lighter and more compact as well as in operation to switch faster in their design here. However, this fully automatic shift aids should not be confused with an automatic transmission with torque converter.
The Actros from Daimler AG offers with the various options Telligent transmission systems, where the next favorable or manually operated gear can be selected by dialing code. The transition is first checked by the electronics for plausibility and then optionally inserted when you step on the clutch pedal. Fully automatic systems, as they were first used at the Iveco Stralis - and the MAN -TGA, even do away with the clutch pedal. Here, the motor speed of the drive - train via electronic instructions is adapted to the injection pump or the engine brake, whereby it is unnecessary to synchronize the transmission. Hybrid systems, like Opti Cruise from the house of Scania, the driver's clutch foot only need for starting or stopping the vehicle.
Most modern commercial vehicles, such as the Actros from Daimler need since built in 2006, due to the modern engine technology, only twelve courses. Installed here is a 3 -speed basic gearbox with forward and rear-mounted. The four control axes ( rotating and sliding rod of the basic gear and the locking bars of pre-and rear-mounted gearbox ) are moved by pneumatic cylinders, being that of the GS unit connected to the CAN bus ( transmission control unit ) monitored and controlled electronically. This also takes over the operation of the clutch by means of hydro- pneumatic components.
The driver enjoys in such vehicles, the comfort, only to have a display in front of him, informed him of the engaged gear (1-12 ), but each can actively intervene in the automatic, for example by keeping the steering Stick lever (MAN), or shift console ( Daimler) manually selects a higher or lower gear. Even a skillful leadership of the accelerator pedal to actively intervene in the automatic switching ( kickdown, etc.).
In designing the gear controls manufacturers follow different approaches: Daimler AG are traditionally in its Actros models. The previous ZF Ecosplit transmission levers owed, there is the shift console of a main knob and a so-called "split- rocker". Pressing the Split - rocker that is caused in the 12-speed setting to change to exactly one of the twelve courses, in truth, a half gear. When you press the shift knob " looking " at the GB control to the next higher or lower self, by matching the load and speed. These courses can also be skipped. Per shift paddles on the dashboard special modes such as rocking, or the marshalling program can be accessed directly.
MAN followed in his TipMatic a different strategy: It is assumed here that the transmission has twelve courses, regardless of how they are composed technically. Knowledge of the pre-and rear-mounted technology sets these producers did not advance, but treated the twelve steps or less sequentially. The driver code base is limited here, whether he wants to go forward or backward, and if he wants to rank or not. This is pre-selected with a rotary switch next to the driver's seat. Per pitman arm can be shifted down or up on the fly each one of the twelve courses. In manual intervention in the switching strategy, the TipMatic ® is not looking for the best gear, but submits himself to the will of the driver.
Silent transitions
In DIN 70020 " motor vehicle; General concepts, definition and explanation " from April 1954 and December 1950, " " defined: " silent passages About quietly working gear pairs running gears (not the direct gear ). " This definition was established in February 1957 in DIN 70020 Part 3 " General concepts in motor vehicle; Capabilities, speeds, acceleration, Miscellaneous " taken over.
Gearboxes for other functions in motor vehicles
Also at other locations outside of the powertrain to find gear: the wipers are moved by an electric motor through gear. The same is true for electric window regulators. The seat adjustment with rotary wheels for backrest angle adjustment via transmission. And opening mechanisms of the doors and hoods, or the transmission of a pedal movement on a vehicle in the engine unit are structurally kinematic sense a vehicle transmission to the pivotal movement of the pedal is converted via a push rod, for example, into a linear movement or a rotary movement. The liquid- bound way of the power transmission between the brake pedal and wheel brake cylinders also represents a hydraulic transmission