Mnemonic
Mnemonics [ mnemotɛçnɪk ], also memory training (from the Greek μνήμη MNEME, Memory ',' memory ' and τέχνη Techne ' art ' ) is an invented word, since the 19th century for ars memoriae and ars reminiscentiae ( " art of memory ") is used usually synonymous with mnemonics (Greek μνημονικά mnēmoniká ). The mnemonics developed memory aids ( mnemonics ), for example as a mnemonic, rhyme, scheme or graphic. Besides small memory aids are among the mnemonics but also complex systems, with which one can surely remind all books lists with thousands of words or a thousand -digit numbers.
History
It is recorded that the orator of ancient Greece and Rome often served mnemonic means. The poet, statesman and world Simonides of Ceos manner was generally regarded as the inventor of the art of memory. Statements to this effect are found in Cicero, Quintilian, Pliny, Aelianus, Ammianus Marcellinus, Suidas and in the Parian Chronicle. The Parian Chronicle is a marble plaque from about 264 BC, which was found in the seventeenth century on Paros and the legendary data from discoveries listed as the flute, the introduction of cereals by Ceres and Triptolemus and the publication of Orpheus seals, as well as in of historical time, especially festivals and awarded prizes listed here. Among them there is also a passage about Simonides: "Since the time when the Keaner Simonides, son of Leoprepes, the inventor of the system of reminders, the choir Price in Athens won and statues were erected in honor of Harmodius and Aristogeiton 213 years. " (which would be 477 BC ).
The story of how Simonides invented the art of memory, Cicero describes quite vividly in his rhetoric textbook De oratore, one of the three main sources about the ancient art of memory: " At a feast which was organized by a Thessalian nobles named Scopas Simonides was one in honor of his host lyrical poem before, which also included a section to the glory of Castor and Pollux. The economical Scopas informed the poet that he would pay him only half the agreed sum for the praises, the rest he should let himself sharing the twin gods to whom he had devoted half the poem. Shortly afterwards, Simonides was brought the news, waiting outside two young men who wanted to speak to him. He left the feast, but could see no one out there. During his absence the roof of the banquet hall caved in, burying Scopas and his guests under the debris. The corpses were so crushed that the relatives who wanted to pick up for burial, they could not identify. But since Simonides remembered how they had sat at table, he was able to show the relatives, who had each their dead. The invisible visitors, Castor and Pollux had paid liberally for their share of the praise by Simonides had removed the banquet just before the collapse. "
The other two major works are institutions oratoria, a rhetoric textbook by Quintilian and the anonymous Ad C. Herennium libri IV latter, Ad Herennium, attributed in the Middle Ages falsely Cicero, formed the patterns on which the numerous medieval texts on the art of memory - more than Some of the rhetoric education - oriented.
Between 410 and 430 AD, Martianus Capella wrote the treatise De nuptiis Philologiae et Mercuriae ( Of the Marriage of Philology with Mercurius ), which essentially retains the seven liberal arts of ancient education system (grammar, rhetoric, dialectic, arithmetic, geometry, music, Astronomy ) represents and thus became a basis of medieval education system. In this document, the memoria forms part of the rhetoric. The church teacher Albertus Magnus in De Bono ( the Good ) and Thomas Aquinas in his Summa Theologiae treated the art of memory, however, in the context of the doctrine of virtue, as a part of Prudence ( Wisdom), a reference that later protected the art of memory before theological attacks. In Thomas Aquinas later almost all authors relied namely to justify and support of their writings.
Simple Example
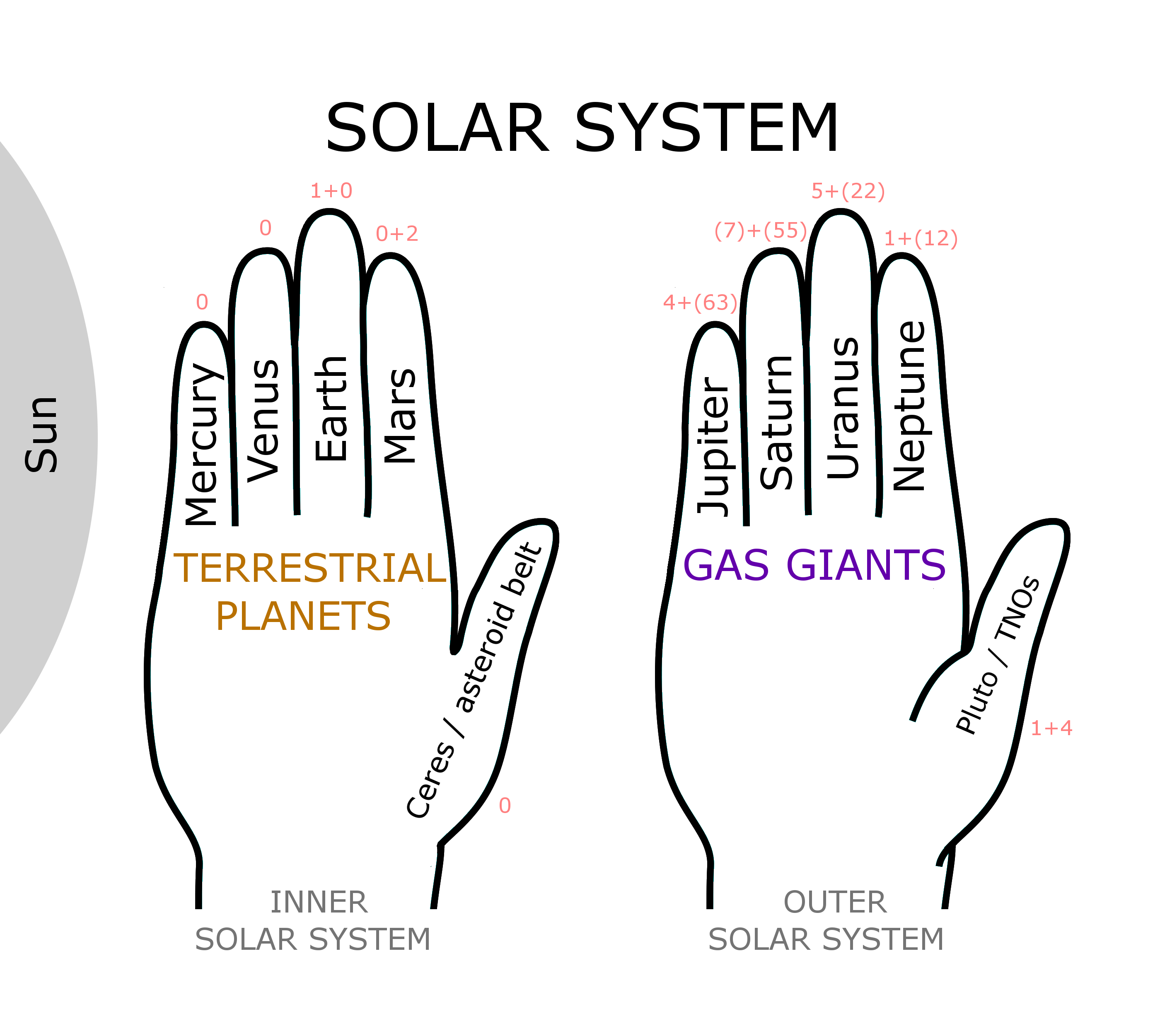
The following sentence can you look at the planets sequence, from the Sun, memorize: "My father explained to me every Sunday our night sky. " Where each of the first letter of a planet with the same initial letter. The M in My for Mercury ( planet closest to the Sun ), the V in father for Venus ( next closest planet from the sun ), and so on for Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The hint requires that you know the planet names. Facilitate learning, just as with the complex systems when the content of the fictional scene that describes the sentence as clearly as possible, lively and colorful imagines. It would be advantageous if one imagines the father, as he explains the planet by means of a drawing in a large book or a blackboard. Of course, with his own father, in the atmosphere and the environment that for the family on Sundays in their own memory or was typical. The inner repeating the sentence should be emphasized at every single word.
This example of a simple mnemonics already contains the two basic elements even the most complicated mnemonic universal systems, namely order / fixed order on the one hand and clear images for both the classification system and for the pinned knowledge.
Another example is: " Klio / me / ter / thal / Eu / he / ur / po / kal " for the 9 muses of classical antiquity: Clio, Melpomene, Terpsichore, Thalia, Euterpe, Erato, Urania, Polyhymnia and Calliope.
Chain method, chains of
In typical methods of mnemonics to learning concepts like links in a chain are attached to each other so that the correct order is maintained. It just comes up with a story containing these terms. The danger is that if a link is lost, the entire chain of association were " tears ". There are also specific methods in which this risk can be minimized.
The methods can be applied to fields of knowledge, which depend on keywords and their completeness and correct order. The most common of these are Digit Symbol systems, the letter system and the method of loci, which is also the oldest system.
Language and vocabulary learning
A familiar word that sounds similar to learning vocabulary is the key word. From the keyword and the meaning of the word, an image is created in the mind.
Learn note names
Children in particular often suffer from the difficulties of relatively abstract learning the note names. A well known example for learning the circle of fifths is the sentence: " You go Age donkey Hole Fish". Assistance by mnemonic approach a visual comparison with child-friendly illustrations. Important is also the choice of images with phonetically more accurate pronunciation, for example " elephant " and not " bucket".
Number symbol system
Further numerical order systems are the number - rhyme system and the broader major system in which the digits are mapped consonants.
Alphabet method
In the case of the alphabet method form the letters of the alphabet, each with a so firmly linked image the memory skeleton, whereby also the converted -to-remember words into images and each connected to a respective image that is fixed for a letter.
The images for each letter but are not ( 1 stands for a candle, a pen or a ruler ) as the simple numerical method from the form, but formed of a word with the same initial letter. When setting up the system, the user can for example choose to remember the word and Lemon image for Z. If again the word " relativity " in the list of words that you want to just remember and stands there next to " Z", then you could imagine again Einstein with a blackboard on the Formulas standing, while he bites into a lemon half and the face contorts. Precisely this picture, in which one yet include smell and taste, is a good example of an image that is hardly forgotten because the brain stores vivid images well. In combination with a characteristic order, here is the letter Z, which makes the memory callable, it is easily possible a list of words to memorize and reproduce in order or play the respective pinned this word in reference to a letter.
Method of loci
A well-known and widely used mnemonic association technique is the method of loci (from the Latin locus for place / space ). It was the main method in ancient and medieval times. To master this technique, it requires very little effort. If you try to remember a sequence of things in a conventional manner, often much gets mixed up in the brain. Use the loci technique, the learning content organized " encoded ".
Its own place in the loci technique is reserved for each term, quasi- created variables that can be assigned to various contents. These variables are in a higher, fixed structure, so that it is possible to maintain the exact order in playback. The fixed structure of which we spoke above, can be a well-known way, but also a space. It does not necessarily have to be a real space in the second case. One can create his own space itself, but this must be done in the greatest possible detail. In both variants, it is necessary to select very unique places where later to remember things can be stored. Then you can place it on the prepared mentally places to watch the end in the form of vivid images; it when you first linked several things on an association image and then stores only mentally is particularly favorable. Thus, " saving space " and is remembered on top of that easily. You can always re- use, almost new " describe " the way or the room.
Indentation by a walk
A well known example
The structure of a typical acquitted speech can be memorized with the front view of a Greek temple. The introduction of speech is associated with the stairs, right, sunlit column with the pro- arguments and the left, shaded column with the counter- arguments. The mean half-shaded column leads similarities or irreconcilable opposites together. The tapered roof of the temple is associated with the final result ( for example, a compromise or a synthesis).
Memory palace
A memory palace is a fictional, existing in the head entity that serves the long-term store of knowledge and to bring its local structure logic into an existing knowledge in the head. It is essentially based on the principle of the method of loci, however, there is at his " construction " some fundamental differences.
Memory principles
The memory works according to certain principles that you should apply for an efficient and possible long-term storage.
Mnemonic Mental Factors
There are seven so-called mnemonic mental factors:
The mnemonic mental factors can be easily imprinted with following characteristics sentence ( acrostic ):
"All Factors Lead To Very Efficient Learning"
( Association, imagination, logic, transformation, visualization, emotion, localization )
General principles of memory
The following principles are, as far as the choice of words, named so that they together form the word colors:
Application Help
The most important step of mnemonics is to imagine the combinations generated images or movies on its inner canvas. So keep your eyes and see before the inner eye. Only then you can reach the best result.


.svg/2000px-Month_-_Knuckles_(en).svg.png)