Arab world
The term Arab World (Arabic: العالم العربي, al Alam al - Arab ), ( therefore mostly sensitive in Arabic ) is not well defined in spite of its wide use, describes a group of regions in North Africa and the Arabian peninsula, geologically part of Africa. It includes states with a majority of Arab culture as a community. There can be several criteria apply to define membership in the Arab world: the predominance of the Arabic language ( linguistic criterion), the influence of Islam (religious criterion ), and finally a member of the Arab League ( political criterion ).
Linguistic criterion
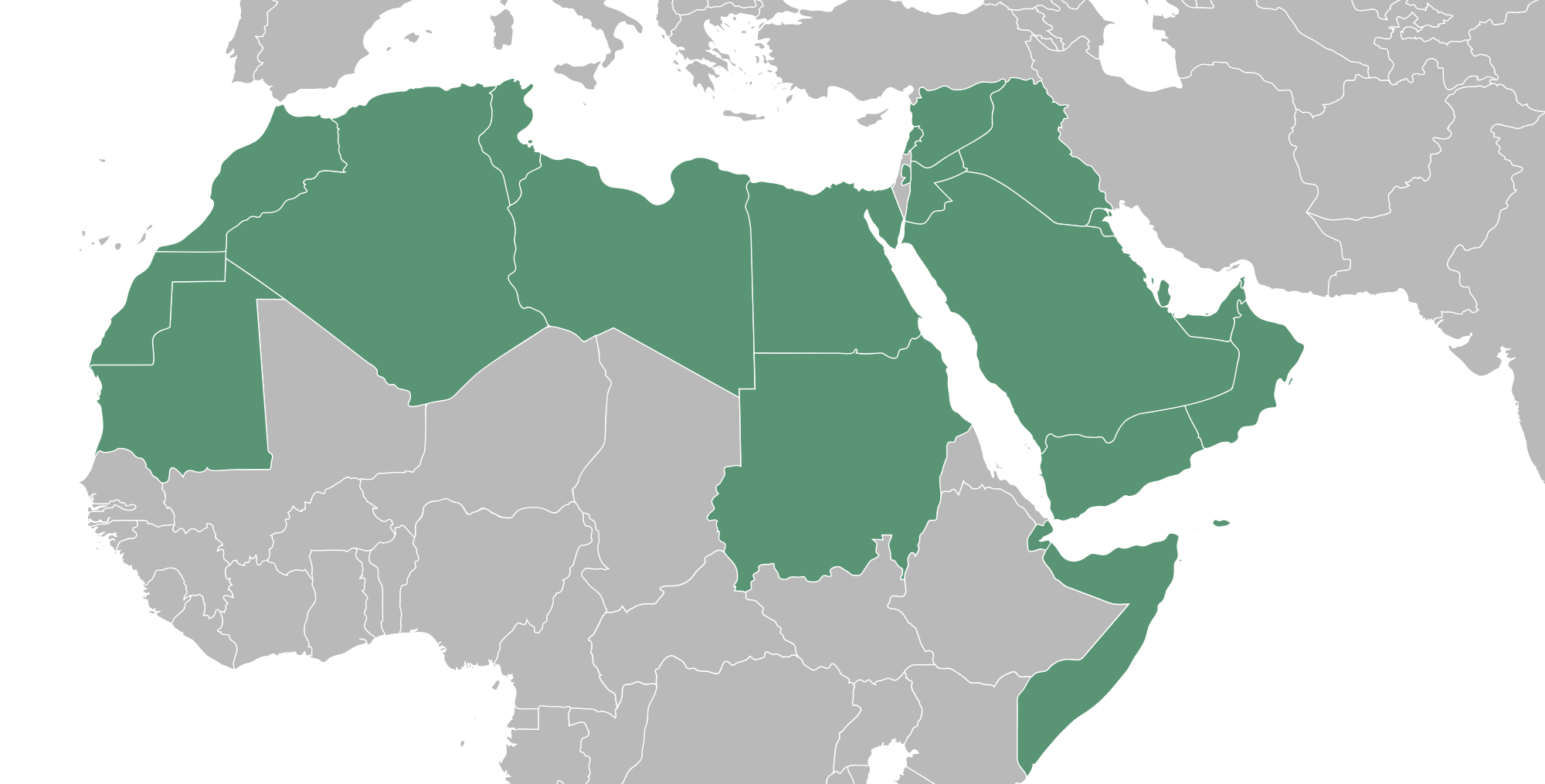
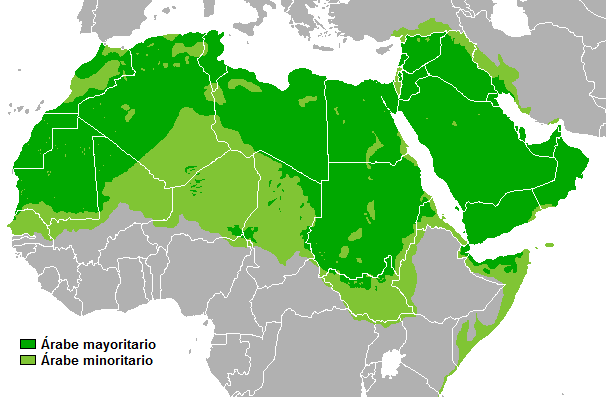
After the linguistic criterion, the Arab world is a group of 24 countries from Mauritania in the west to the Sultanate of Oman in the east and 2 are not sovereign territories. The spread of Arabic is largely due to the history of the spread of Islam in the 7th century. However, the linguistic criterion is not sufficient to consider the Arab world. Some countries where Arabic is spoken, still are not considered part of the " Arab world ", including Malta, Israel, Somalia, Djibouti, Eritrea and Chad, as a rule.
The following list outlines 26 sovereign states and non- sovereign territories where the Arabic language is spoken. Countries with an Arab majority are highlighted. The United Arab Emirates are generally regarded as part of the Arab world, though the Arabs put there in the general population that is minority. Foreign citizens are therefore excluded in the table there.
Religious criterion
Related to the concept of the Islamic world. The Arabs are in the Islamic world in the minority, although Islam comes from Arabia and is passed on and preached in Arabic.
Arabism is defined independently of religious affiliation: Arabs can be Muslims, but also Christians and atheists. In Lebanon have entire regions (such as the three administrative districts Kesrouan, Metn and Jabal Lubnan ( Mount Lebanon ) ) is a closed Arab Christian population structure until a few decades ago they put there even the majority.
The pan-Arabism is the recruiting ground of Islamism, but the persecuted ideological objectives other than the nationalist pan-Arabism, and in contrast to this the Christian element of the Arab world negated and denies its autochthonous character. In the pan-Arab movement, many Arabs from Christian families were above-average activity, in addition to Michel Aflaq ( Syrian founder of the Baath Party) and Elias Farah ( Syrian- Iraqi Baathist ideologue ), for example, in 1949, executed in Lebanon SSNP - founder Antun Saada in 2005 murdered Lebanese Communist Party General Secretary of the Lebanese Communist Party George Hawi and ( Marxist ) PLO leader George Habash as.
The political criterion
The term can on the one hand all the Member States of the Arab League ( and its inhabitants ), on the other hand, the continuous settlement of the Arabs or the al - watan al - arabi (Arab fatherland ), respectively.
The two concepts are not identical, since there are both Arab minorities in countries which are not members of the Arab League ( such as Turkey and Iran or Israel), as well as Member States that do not have clear Arab majority, such as Somalia, Djibouti or the Comoros. To the Arab homeland but are mostly nationalists and the Iranian province of Khuzestan, the Sanjak of Alexandretta ( Iskenderun ), the Western Sahara and Eritrea, although these areas do not belong to the league. At least from Libyan vision also includes Malta to the Arab world.
Politically there is in the Arab world the common dream of a united Arab nation in a state. All previous attempts agreement of pan-Arabism but are unsuccessful. Known pan-Arab thinkers and leaders of the modern era are Michel Aflaq, Gamal Abdel Nasser and Muammar al - Gaddafi, as well as the PLO sees itself as the spearhead of Arab unity movement in the idea that the Palestinian revolution may be the trigger of the Arab revolution. Not least because of this view is the Middle East conflict formative not only for Israel, but regularly moved the Arab masses.
The Arab League is an association of Arab States, was founded on March 22, 1945 in Cairo and consists of 22 Member States.
Economic and social situation
Most Arab countries are emerging or developing countries. The exceptions are the countries Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain and the United Arab Emirates, which are industrialized countries today.
In the countries of the Middle East 's economy has grown according to the World Bank between 2000 and 2006 by an average of 5.31 percent per year. Gross national income of all 22 countries of the Arab League in 1999 was $ 631.2 billion. In 2006, the gross national product rose to 1.585.14 billion. Saudi Arabia has the largest gross domestic product in the Arab world.
Geographical classification of Arab States
The North African states on the Atlantic and the Mediterranean coast that have been Arabized only later and more or less strong traditions of other tribes ( Berbers, Tuareg ) have:
- Mauritania
- Morocco
- Algeria
- Tunisia
- Libya
The Nile countries with ancient farming tradition:
- Egypt
- Sudan
The countries of the Horn of Africa who possessed intense connections to southern Arabia since ancient times:
- Somalia (since 1991, Somaliland split from Somalia)
- Eritrea ( not a member of the Arab League )
- Djibouti
- Comoros
The countries on the Arabian Sea and South and Central Arabia:
- Bahrain
- Yemen
- Qatar
- Oman
- Saudi Arabia
- United Arab Emirates
- Kuwait
The states of the Levant and North Arabia:
- Iraq
- Jordan
- Lebanon
- Palestine
- Syria
- Israel
The Arab Maghreb Union ( AMU)
The Nile and its tributaries and its countries
Horn of Africa
Arabian Peninsula
Arabian Sea