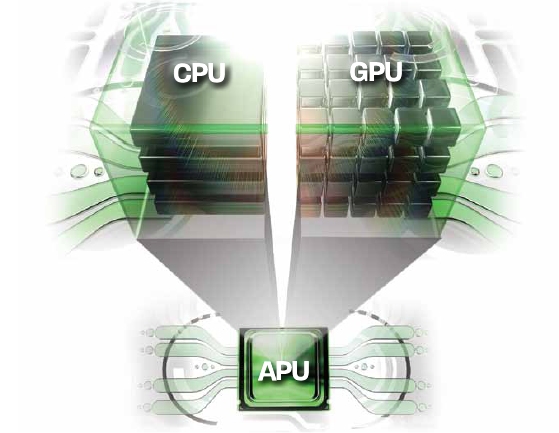
Accelerated Processing Unit
Accelerated Processing Unit (aka " APU ", English for " accelerated processing unit " ), and Advanced Processing Unit (English " advanced processing unit ") is an ajar among others, the abbreviations "CPU " and " GPU " name for a main processor with integrated coprocessors. As the name suggests, should be accelerated in certain situations, the main processor through the / coprocessor (s). As a co-processor can serve a graphics processing unit (GPU ), vector processor, stream processor or any other arbitrary processor is superior to the main processor in certain situations. Only a math coprocessor in the form of a floating point unit (also called " FPU " for short ), which - among other - was integrated into the main processor long before the definition of the APU concept and thus became part of the main processor is exempt.
History
Created and was coined the term Accelerated Processing Unit from the microprocessor manufacturer AMD, which uses this designation to distinguish main processors with integrated graphics unit. AMD Fusion is the code name of this processor concept that CPU, GPU, video and other hardware accelerator brings together on one die.
First announcements for the integration of a GPU core in a main processor it had in 2006, following the acquisition of ATI by AMD, given. From May 2010 prototypes were delivered to the first customers at Computex in spring 2010, it was announced that the APU Llano and Ontario models to come on the market in the first half of 2011. Moreover, it was known prior to the CES 2011 that first computer in the form of tablet PCs and computers are shipped based on the APU Zacate and Ontario series in the first quarter of 2011.
Intel has also introduced APUs in 2012. So the GPU is supporting the establishment of OpenCL and DirectCompute for universal computer calculations in the Ivy Bridge processors.
Technical details
The combination of multi-core processors will contain one or more main processing cores (CPU) and at least one additional co-processor for specific tasks. The additional coprocessor is for now a graphics processor ( GPU). With this concept, one wants to unite especially the advantages of different types of processors / processor architectures. The concept itself is therefore also based on multi-core processor systems as a heterogeneous computing ( english: heterogeneous computing ) because now occur heterogeneous processor types in one system.
Since graphics processors in the course of their evolution tasks a part of their specialization in graphics and increasingly becoming programmable processors were able to edit the particular data-parallel tasks very quickly, saw here the manufacturers the option optimized for sequential tasks CPUs useful with this type of coprocessor supplement. Moreover, since each PC anyway requires a graphics processor, should the transition in time, is missing in the software that runs on the coprocessor, be bridged by the pure benefits of a graphics processor.
Decisive for the name APU is therefore not only the integration of a graphics processor in the main processor, but also the suitability of the GPU's processor cores for the calculation of universal tasks away from pure graphics calculations.
GPUs have been used very early for GPGPU purposes, but the programming was done very close to the hardware and could thus not be transferred to other GPUs readily, making the broadcasting of such programs and tools remained very limited. Another important step from a pure main processor with IGP to so-called APU is thus the support of cross-vendor programming standards such as OpenCL and Direct Compute Quasi standards such as the DirectX 11 API on graphics processor.
Away from the programmable GPU parts, the GPU but also has hard-wired units (English: Fixed Function Units ) that can be used away from the graphics. Thus, the video decoding units such as UVD or Nvidia video processor can be used for a long time for the decoding of certain codecs and thus also relieve the main processor. Intel's integrated GPU in Sandy Bridge CPUs have off such decoding units also hardwired Encodiereinheiten with which the encoding of videos can be accelerated in certain codecs. Since both the encoding and decoding but only limited to certain codecs and are not programmable, corresponding CPUs are in a strict interpretation of the APU - definition still referred to as " CPUs with IGP and additional acceleration functions" and not as APUs, since in this case the concept of connecting multiple processor architectures with different advantages and lacks only one processor architecture is specialized by hardwired units on some areas.